* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pits - Botany and Plant Pathology
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
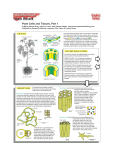
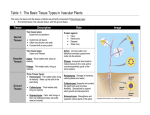
Plant Structure Bot 313 Lecture 2 1.Introduction to the sporophyte plant body 2.Cells, cell wall, & cell types 3.Parenchyma & Collenchyma 4.Concepts of “sameness” Homology & Analogy Recap: Alternation of phases (generations) Recap: Alternation of phases (generations) The Plant Sporophyte Construction of the plant body (sporophyte) • Plant body • Organs (stem, leaf, root, sporangium) • Tissues (Tissue Systems) (dermal, vascular, ground) • Cells (parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma) Construction of the plant body (sporophyte) • Plant body • Organs (stem, leaf, root, sporangium) • Tissues (Tissue Systems) (dermal, vascular, ground) • Cells (parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma) Plant Cells and Cell Walls Middle lamella, Primary wall, Secondary wall Construction of plant cell walls • • • • • • Cellulose fibers Hemicellulose Structural proteins Enzymatic proteins Carbohydrates (also lignin in secondary walls) Cells held together by Middle Lamella (pectin) Plant Cells and Cell Walls Middle lamella, Primary wall, Secondary wall Thin areas in plant cell walls = Pits Openings in plant cell walls connect adjacent cells = Plasmodesmata Cell walls Primary pit field White= middle lamella Blue = primary wall Brown = secondary wall depressions in 20 wall=pits Pits and plasmodesmata Plasmodesmata= cytoplasmic connections Pit= Depression in the 2o wall Opposing pits= pit pairs Pit membrane= thin part of wall Primary pit field (primordial pit) in cells with 1o wall = thin place in the wall penetrated by plasmodesmata Circular bordered pits Half-bordered pits Torus=thickening of the pit membrane Margo= surrounding part of the membrane Parenchyma • • • • • Uniformly thin primary wall Alive at maturity Readily re-differentiated into other cell types Involved in photosynthesis, storage and secretion Found in pith, outer cortex of stems and roots, vascular bundles, leaf mesophyll and in flesh of fruits • Also found vascular tissue (xylem and phloem parenchyma, ray cells, etc.) Parenchyma cells Primary wall of cellulose Stains green with Fast green stain Note: intercellular spaces & shapes of cells Uniformly thin primary wall only Living at maturity Readily re-differentiated Storage Photosynthetic Common in all tissue types Parenchyma • Relatively unspecialized • Can still undergo cell division – Large vacuoles • Important in regeneration and wound healing Parenchyma cells in a root Parenchyma cells in Aglaophyton major From the Lower/Middle Devonian (400 MYO) Rhynie Chert from Taylor et al, 1995 from Edwards 1986 Collenchyma • • • • • Differentially thickened primary wall Alive at maturity Limited re-differentiation into other cell types Support function Found in ground tissues of stems and leaves Collenchyma • Differentially thickened primary wall • Alive at maturity • Elongated • Support tissue Parenchyma and Colllenchyma cells in stem of Helianthus (x.s.)