* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ground Tissue
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
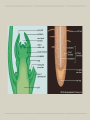
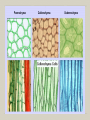
Celery Lab Follow Up Capillary Action Xylem Transports water From roots to shoots Osmotic Pressure Water will flow from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration The net movement of water into or out of a cell produces a force Tissue—Ground Tissue Botany 1 Mrs. Russell Objectives Know the three tissue systems in plants Know the meristems present in a plant and where they are found. Learn tissues of the plant that are neither meristematic nor function in conducting at maturity Be able to identify the types of ground tissue under the microscope Tissue Systems Dermal Tissue (the skin) Epidermis Vascular Tissue (the bloodstream) Xylem Phloem Ground Tissue (everything else) Parenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma RAM and SAM Meristem = regions of tissue that are capable of growing into a new plant part (embryonic), mitosis is happening Primary meristem—shoots or roots grow longer Secondary meristem—shoots or roots grow larger in diameter (woody plants) Root Apical Meristem (RAM)—at the tip of the root Stem Apical Meristem (SAM)—at the tip of the shoot Types of Ground Tissue Cells Collenchyma Parenchyma Sclerenchyma Collenchyma Think strings in celery Elongated cells Structural support Living cells with irregularly thickened walls Parenchyma Soft parts of the plants Forms cortex, pith, mesophyll, pulp of fruit and endosperm of seeds Living cells with thin, flexible cellulose cell wall Sclerenchyma Supporting tissue Fibers and sclerids Source material for fabrics Dead cells with extremely thick cell walls Lab on Monday