* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Magic mushrooms (L)
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Effects of long-term benzodiazepine use wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Urban legends about drugs wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
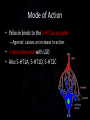
Magic Mushrooms Aka Shrooms, Mushies, Boomers Psychedelics • Drug category • Types – Lysergamides (eg. LSD aka acid) – Indolealkylamine (eg. Shrooms) – Phenylethylamine (eg. Molly) • Primary Receptor – 5-HTa: serotonin-like • Mood, Hallucinations Mushrooms • Indolealkylamine (eg. DMT) • Contain psilocybin and psilocin – primary hallucinogenic component – Isolated by Albert Hoffman in 1958 • Used in ancient times for spiritual rituals • Schedule 1 (most illegal) since 1970 • Potency varies between: – Species – Same Crop – Same mushroom (eg. Cap v Stem) Pharmacokinetics • Predominantly ingested – Fresh mushroom, dried, powdered, encapsulated – Slower onset compared to smoking, injecting • 10-40 min onset – Longer lasting compared to smoking, injecting • Lasts 3-8 hours Acute Effects • • • • • • Elevated sense (auditory, visual, emotions) Hallucinations Altered time perception, disorientation Euphoria at lower doses Anxiety at higher doses Limited dopamine release Mode of Action • Psilosin binds to the 5-HT2a receptor – Agonist: causes an increase in action • Cross tolerance with LSD • Also 5-HT1A, 5-HT1D, 5-HT2C Withdrawal • Hallucination Persisting Perception Disorder (HPPD) • No significant long-term health effects • Insignificant withdrawal relatively • Flashbacks Treatment • Acute (right away, for overdose) – No immediate way to undo “bad trip” – Benzodiazepines can be used for agitation • Chronic (long term) – Considered not addictive