* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kidney Transporters
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
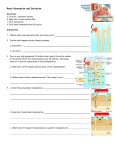
PROXIMAL TUBULE Substance Glucose Transport Mechanism Tm Reabsorption (secondary active transport) Apical Membrane SGLT2 and SGLT1 Na-glucose co-transporters (specific for D isomer) Na-Pi co-transporter Basolateral Membrane -Na/K+ ATPase (Na+ gradient) -Transporter to move glucose out -Na/K+ ATPase (Na+ gradient) -Pi-anion co transporter Inorganic Phosphate Tm Reabsorption (secondary active) Amino Acids Tm Reabsorption (secondary active) Tm Reabsorption (secondary active) Non-Tm reabsorption Basic, acidic and other (3 types) transporters -Na-H exchanger (NHE-3) secretes H+ at apical membrane by secondary active transport -H-ATPase secretes H+ at apical membrane via primary active transport -Na/K+ ATPase (Na+ gradient) -Na-3HCO3- co-transporter Non-Tm reabsorption -Reabsorbed between cells in early PT (solvent drag) -Reabsorbed through cells late in PT Non-Tm reabsorption (passive) Base/Anion-Cl- exchanger coupled to Na/H+ exchanger causes Cl- to enter cell (tertiary active transport) -Na/K+ ATPase (Na+ gradient) -Cl- channel or bicarbonate exchanger Reabsorbed through or between cells (solvent drag) Organic Anions (PAH, uric acid, radiologic contrast media, furosemide, penicillin) Tm secretion (tertiary active transport) Organic Cation Tm secretion (secondary active) -MRP2 pumps anion out to TF linked to NaDC1 which brings alphaKG and 3 Na+ in -electrogenic anion transporter -anion exchanger -organic cation:H+ exchanger puts OC into TF (H+ enters cell down EC gradiet) -Na/K ATPase prevents K+ from leaving cell down at basolateral membrane -OAT1 moves organic anion into cell for alphaKG -NaDC3- alphaKG back into cell with 3 Na+ - Na/K ATPase Metabolic Intermediates Bicarbonate Na and Cl K+ -OCT brings cation into cell down EC gradient Regulation -Kidney helps regulate Pi levels by excreting Pi in the urine when levels exceed threshold -PTH lowers Tm and increases GFR, decreasing threshold and increases excretion -Carbonic anhydrase activity (if low, will decrease reabsorption) -pCO2 (if increased, will increase reabsorption) -Amount of HCO3- filtered (more filtered means more reabsorbed) -Catecholamines increase proximal Na+ reabsorption -ANF decreases Na+ reabsorption