* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2b Packet
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
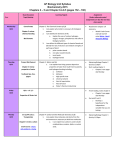
Chapter 2b Packet Name ______________________Date _____________ Period _____ 2b Quiz Study Guide (___________________) Using the table below, be able to identify which group of organic molecules each function, picture, building block or example goes with (see practice quiz/video notes for more information). Organic Molecules Carbohydrates Function Short term energy storage, Support Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Long-term energy storage, Cell membrane, Water-proofing, Insulation Transport, Movement, Speed’s up chemical reactions, Support Control’s cell’s activities, Carries hereditary info, Makes proteins Picture Building Blocks Monosaccharides (glucose, fructose) Glycerol and fatty acids Amino acids Nucleotides Examples Lactose, Sucrose Starch, Glucose, Fructose Glycogen Cellulose Phospholipids Waxes, Steroids Saturated Fats Unsaturated Fats Enzymes Antibodies Actin/Myosin Keratin DNA RNA Ch. 2b Test Study Guide (________________) Know the definitions of the words: energy, work, organic compounds, enzymes, fiber, glycogen, starch, cellulose, products, reactants, nucleotides, amino acids, substrates, active site, saturated fats, unsaturated fats, lipids, ATP, macromolecule, monomer, polymer, and subunits. Understand there are four basic groups of macromolecules or polymers that make up in living things. Know the functions of each group of organic molecules. Be able to identify pictures of the four groups of molecules or their building blocks (monomers). Be able to identify the building blocks (monomers) of each group. Be able to identify examples from the notes, labs, and text from each group. Understand how enzymes work and be able to identify the parts of an enzyme-substrate complex including the active site, products, and reactants allosteric inhibitor and competitor. Understand that temperature and pH can influence the rate of enzyme action. Be able to interpret/analyze graphs looking at enzyme dynamics. Ch 2b Reading Guide: Pages 34-37: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic Acids 1. ____________ compounds contain carbon atoms that are covalently bonded to other elements—typically hydrogen, oxygen, and other carbon atoms. 2. ________ main classes of organic compounds are found in living things: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. 3. _________________ are a key source of energy, and they are found in most foods—especially fruits, vegetables, and grains. 4. The building blocks of carbohydrates are single sugars, called monosaccharides such as _________ and _____________. 5. Disaccharides are double sugars formed when _______ monosaccharides are joined. 6. Polysaccharides such as starch are chains of __________ or more monosaccharides. 7. There are two polysaccharides that store energy. __________ is made by plants. ____ ___________, which is made by animals. Both are made of hundreds of linked glucose molecules. 8. ____________________ is a polysaccharide that provides structural support for plants. Humans cannot digest it. This is the “fiber” in our diets. 9. _____________ are nonpolar molecules that are not soluble in water. They include fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. 10. Phospholipids make up the lipid bilayer of _____ membranes. ___________ include cholesterol, which is found in animal cell membranes 11. ________ are lipids that store energy. 12. Most animal fats—such as those in butter, lard, and grease from cooked meats—contain primarily __________________ fatty acids. (solid at room temperature) 13. Most plant oils, such as olive oil, and some fish oils contain mainly __________________ fatty acids and are generally liquid at room temperature. 14. A ______________ is a large molecule formed by linked smaller molecules called amino acids. 15. ____________ ____________are the building blocks of proteins. ______ different amino acids are found in proteins. 16. Proteins have many different functions such as (list 3) _________________________________________. 17. Smaller molecules that make up nucleic acids are called ____________________, which has three parts: a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group. 18. There are two types of nucleic acids—_________ and ________. 19. _____________________ contain long strands of DNA, which stores hereditary information. Pages 38-42: Energy and Chemical Reactions 1. _____________ is the ability to move or change matter. 2. List at least four forms of energy. 1. __________________ 3. __________________ 2. __________________ 4. __________________ 3. A ____________ __________is a process during which chemical bonds between atoms are broken and new ones are formed, producing one or more different substances. 4. The starting materials for chemical reactions are called __________________. 5. The newly formed substances are called __________________. 6. Chemical reactions are summarized by chemical __________________, which are written in the following form: Reactants → Products 7. __________________ is the term used to describe all of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism. 8. Your cells get most of the energy it needs from _____________. 9. The energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called __________________ __________. (chemical push) 10. ________________ _______________ are chemical reactions that occur in cells. 11. ______________ are substances that increase the speed of chemical reactions. 12. Most enzymes are ________________. 13. Enzymes are also called _________________, substances that reduce the activation energy (chemical push) of a chemical reactions. 14. A substance on which enzymes react during a chemical reaction is called a _______________. 15. An enzyme’s __________ determines its activity. 16. The folds or pockets are called the __________________ ___________. Each enzyme only works with a specific substrate that fits into its active site. 17. Any factor that changes the _____________ of an enzyme can affect the enzyme’s activity. 18. List two factors that can affect an enzymes activity. 1. _____________________ 2. _________________ Chapter 2b Notes Section 3 Carbon Compounds Macromolecule means “large molecule”; four main groups of polymersCarbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids Each polymer is made of individual building blocks called monomers or subunits. Organic Molecule Group A. Carbohydrates- organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen Function and oxygen atoms in the ratio 1:2:1 Function - Short term energy storage, support Building Blocks Examples: --Monosaccharide: building blocks of all carb. - simple sugars; glucose and fructose - C6H12OExamples 6 --Polysaccharides: Large compounds to store energy; starch (plants) and glycogen (animals) and Cellulose is a polysaccharide used for support B. Lipids: non-polar molecules that are not soluble in water Function-- Long-term energy storage, cell membrane, water-proofing, insulation --made of glycerol and 3 fatty acids Examples: Phospholipids (make up cell membrane), steroids (strengthen cell membrane), waxes, oils, pigments (chlorophyll) C. Proteins- Large molecule formed by linking amino acids together Examples-enzymes, collagen (skin, ligaments, tendons, bones), hair, muscle, etc. Function: Transport, movement, speed’s up chemical reactions, support D. Nucleic Acids- long chain of smaller molecules called nucleotides - Has 3 parts 1) Sugar (deoxyribose/ribose) 2) Base (A,G,C,T/A,G,C,U) 3) Phosphate (PO4) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- genetic code, double stranded RNA (ribonucleic acid)- single stranded Function: Control’s cell’s activities, carries hereditary info, makes proteins E. ATP- energy for all cells (energy is in the bonds of the phosphate) Section 4 Enzymes- proteins that increase the speed of chemical reactions (biological catalysts) --Substrate- substance on which an enzyme acts during a chemical reaction --Active sites- substrate and enzyme fit together here --Competitive inhibitor- something that binds to the enzyme at the active site, but is different than the substrate --Allosteric inhibitor- when something else binds to the enzyme that slows down the binding of the substrate ENZYMES operate more efficiently within a range of temperatures and pH ENZYMES ONLINE! Answer the questions _______________ as you go through the web activity. An (*) indicates that there is NO question attached to the number. Read the introduction, paying careful attention to the words: protein, specific, “not changed”, shape, denaturing, FROM THE ENZYME MENU, Select “Why Enzymes?” 1. Click “Without Enzymes” and click “Play” to watch the animation. What happens to the two sugar molecules? _____________________________________________________________________ 2. Click “With Enzymes” and “Play” to see the reaction. What happens to the sugar molecules this time? __________________________________________________________________________ 3. Click “Play” again to see more details about the reaction. What happens to the enzyme? _______________________________________________________________________________ Go back to the ENZYME MENU and click “Specifications” 4. What does it mean for an enzyme to be “specific”? _______________. 5. Click “Play” a couple of times to see the entire chemical reaction take place, then describe in your own words, WHY the sugar required a specific enzyme. __________________________________ _______________ _______________________________________________________________ 6. Click “Play” again to see a reaction that WILL use the green enzyme, then click “Enzyme menu” to go back.* Go back to the ENZYME MENU and click “Reusing Enzymes.” 7. Click “Play” to see two small sugars fit into the enzyme. Then click “Play” again. What happens this time? ________________________________________________________________________ 8. And the time after that? (You have to click “Play” to find out.) _____________________________ 9. What is formed at the end of the process? ______________________________________________ Go back to the ENZYME MENU and click “Denaturing” 10. Click “Play” a few times to see the diagram show how enzymes MUST be a specific shape in order to work.* 11. What happens to the enzyme if it is heated? _____________________________________________ 12. What happens when the small molecules “try” to fit? _____________________________________ Practice Quiz Match the functions with the correct molecule. _____water-proofing _____Long-term energy storage _____Transport, movement _____insulation _____support _____Control’s cell’s activities _____speed’s up chemical reactions _____cell membrane _____Short term energy storage _____carries hereditary info _____makes proteins Match the building blocks with the correct molecule. _____Amino acids _____Glycerol and fatty acids _____Monosaccharides _____Nucleotides Match the examples with the correct molecule. _____Waxes _____Lactose _____unsaturated Fats _____Keratin _____Sucrose _____Glycogen _____Steroids _____Enzymes _____Starch _____DNA _____saturated fats _____Cellulose _____RNA _____Antibodies _____Phospholipids _____Actin _____Myosin C. Carbohydrate L. Lipid P. Protein N. Nucleic Acid C. Carbohydrate L. Lipid P. Protein N. Nucleic Acid C. Carbohydrate L. Lipid P. Protein N. Nucleic Acid Match the pictures with the correct molecule. C. Carbohydrate L. Lipid P. Protein N. Nucleic Acid Chapter 2b Extra Practice1. All organic compounds contain ______________. 2. Without ____________, organisms could NOT maintain homeostasis, carry out chemical reactions, make their own food. 3. The ability to move or change matter is ____________________. 4. All living things require a source of ____________________ to carry out their life activities. 5. The starting materials for chemical reactions are called ____________________, while the new substances that are formed are called ____________________. 6. The energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called __________________ ________________. 7. A chemical reaction can be sped up by adding a substance called a(n) ____________________, which lowers the amount of activation energy required to start the reaction. 8. The portion of an enzyme molecule into which a specific substrate can fit is called the ________ ______. 9. Trypsin is a(n) __________________ that aids in digestion by helping to break down the foods we eat. 10. Foods that are high in fiber most likely come from_________. 11. _________ stores energy for cells to use in the bonds between its phosphate bonds. 12. Olive oil and fish oil are examples of __________________ fatty acids. 13. Lipids that are solid at room temperature are __________________ fats. 14. DNA and RNA are made up of ______________, which contain a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group. 15. Protein folding is determined by the sequence of the __________ _________. 16. Examples of _____________ in your body include collagen and hemoglobin. 17. Monosaccharide, glycogen, cellulose are terms is associated with __________________. 18. The speed of a chemical reaction is increased by an _____________. 19. __________ stores heredity information 20. Two carbohydrates that store energy are __________________, which is produced by plants to store energy, and _____________________, which is produced by animals to store energy. 21. In nucleotides, the letters A, T, C, and G represent ________________ _________. 22. A substrate attaches to the___________ _____ of an enzyme. 23. Temperature and _________ can affect enzyme activity. 24. ________________ a class of organic compounds that includes fats, steroids, and waxes. 25. The building blocks of proteins are ________________; carbohydrates are _______________; nucleic acids are ___________________; and lipids are ________________ and _________ ________. 26. __________________ provides temporary storage of energy for cells. 27. ______________ reduce the activation energy of chemical reactions. SOL Questions 28. The graph to the right represents the relationship between pH and the rate of enzyme action for two enzymes, X and Y. Which statement best describes this pattern of enzyme action? a. As the pH increases from 2.5 to 3.5, the rate of action of enzyme X decreases. b. At a pH of 5.5, the rate of action of enzyme X is the same as that of enzyme Y. c. As the pH increases from 10 to 11, the rate of action of enzyme Y increases. d. At a pH of 7.0, the rate of action of enzyme Y is less than that of enzyme X . 29. This graph to the right shows that a. pepsin is less effective at low pH than trypsin. b. trypsin is not effective at a high pH. c. pH affects the activity rate of enzymes differently. d. more enzymes are present at a higher pH. 30. According to the graph, addition of the enzyme amylase causes the reaction to — a. speed up b. slow down c. take in heat d. give off heat Base your answers on questions 31-34 on the organic compounds represented below and your knowledge of biology. A. B. C. D. 31. 32. Which compound represents the basic unit of both a DNA molecule and an RNA molecule? _______ Which compound contains both an amine group and a carboxyl group? ___________ 33. Which macromolecules are made up of repeating units of molecule D? a. proteins and nucleic acids c. fats and oils b. hemoglobin and enzymes d. starch and cellulose 34. Which food contains the highest percentage of the type of molecule represented by C? a. butter b. bread c. table sugar d. lettuce 35. Lactase is an enzyme that breaks down Lactose in cells. It accomplishes this because of its structure. What part of the enzyme is involved in catalytic activity? a. Binding pocket b. Pleated sheet c. Quaternary structure d. Active site 36. Enzymes only work with specific substrates because each substrate — a. actively interferes with other substrates around it b. has a specific activation site for enzyme attachment c. can only use a specific ionic bond with the enzyme d. destroys its specific enzyme Use the following terms for these 2 diagrams: Substrate, product, enzyme, active site, enzyme-substrate, complex . 37. On the basis of the above graph, at which temperature did the catalase exhibit the greatest activity? _______ 38. Why did the activity of catalase decrease as the temperature continued to increase above 40oC? __________ _________________________________________________________________________________________