* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Variation and Inheritance – Revision Pack (B1) Inherited
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
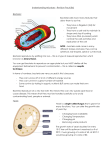
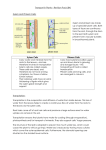
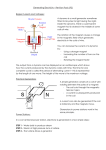
Variation and Inheritance – Revision Pack (B1) Inherited characteristics: Some human characteristics, such as facial features and eye colour, can be inherited. They can be either dominant or recessive. Alleles are different versions of the same gene. Many people believe that intelligence, sporting ability and health are inherited factors, while others believe that the environment in which someone lives influences these characteristics. This debate is known as “nature vs. nurture”. Dominant and recessive characteristics are dependent on dominant and recessive alleles. Dominant alleles will be noticed if they are present, but recessive alleles are only noticed in the absence of the dominant allele. NOTE – a gene can have two different alleles. Chromosomes: Most body cells will have the same number of chromosomes. The number will depend on the species of organism. Human cells have 23 pairs (46 chromosomes in total). Sex chromosomes determine sex in mammals. Females have identical sex chromosomes (XX). Males have different sex chromosomes (XY). A sperm will carry EITHER an X OR a Y chromosome. All eggs will carry an X chromosome. X XX XX X X Y XY XY There is a random chance of which sperm will fertilise the egg. There is therefore a 50-50 chance that the offspring will be male or female. Genetic Variation: Genetic variation is caused by: 1) Mutations, which are random changes to genes or chromosomes 2) The rearrangement of genes during the formation of gametes (sex cells) 3) Fertilisation, which results in a zygote (fertilised ovum) with a mix of alleles from the mother and the father A Monohybrid Cross: b b B Bb Bb b bb bb The diagram expressed to the left is a monohybrid cross showing the likelihood of having a child with blue eyes (bb) or having a child with the recessive blue eye allele but not actually blue eyes (Bb). The recessive alleles are represented by lower-case letter and the dominant alleles are represented by upper-case letters. Variation and Inheritance – Revision Pack (B1) Homozygous means having the same alleles (e.g. bb), while heterozygous means having different alleles (e.g. Bb). A genotype is the person’s genetic makeup, for example if they had blue eyes, their genotype would be bb. A phonotype is how this is actually seen as a characteristic, or which alleles are actually expressed, for example, using the above example; the person’s phonotype is blue eyes. Inherited disorders: Inherited disorders are caused by faulty genes. There are many personal and ethical issues when it comes to finding out that a parent carries a faulty gene: - For example, deciding whether or not to have a genetic test – a positive result for a faulty gene could alter lifestyle and career For example, deciding whether you want to marry and whether you should take the risk and have a child Inherited disorders are caused by faulty alleles, which are almost always recessive. Variation and Inheritance – Revision Pack (B1) Past Papers: PPQ(1): PPQ(2): Variation and Inheritance – Revision Pack (B1) Variation and Inheritance – Revision Pack (B1) PPQ(3): Variation and Inheritance – Revision Pack (B1) PPQ(4): PPQ(5): Variation and Inheritance – Revision Pack (B1) PPQ(6): PPQ(7): Variation and Inheritance – Revision Pack (B1) Mark Schemes: PPQ(1): PPQ(2): PPQ(3): PPQ(4): Continued on next page... Variation and Inheritance – Revision Pack (B1) PPQ(5): PPQ(6): PPQ(7):