* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell-Division
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
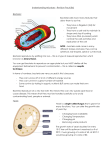
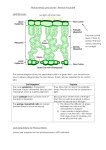
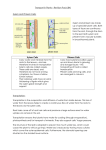
Cell Division – Revision Pack (B3) Multicellular: Advantages of being multicellular: • allows organism to be larger • allows for cell differentiation • allows organism to be more complex. Becoming multi-cellular requires the development of specialised organ systems, limited to: • communication between cells (nervous system) • supplying the cells with nutrients (digestive system) • controlling exchanges with the environment (respiratory and excretory system) Mitosis New cells for growth are produced by mitosis, new cells are genetically identical because they contain the same genetic information – it is a copied cell. Body cells are DIPLOID (contain two copies of each chromosome). The first step, before cells can divide is to replicate the DNA. This is done by: - ‘unzipping’ the chromosome to make it into single strands New strands forming by complementary base pairing The following steps happen in mitosis: 1) The chromosomes line up in the centre of the cell 2) They then divide; or are divided by an enzyme 3) The two copies move to two poles of the cell These cells are genetically identical. Cell Division – Revision Pack (B3) Meiosis: Gametes are produced by meiosis. Gametes are haploid (contain one chromosome from each pair). In meiosis, the chromosome number is halved and each cell is genetically different because: • One chromosome from each pair separate to opposite poles of the cell in the first division • Chromosomes divide and the copies move to opposite poles of the cell in the second division. Fertilisation results in genetic variation because: Gametes and Fertilisation: - - The two gametes (egg and sperm cells) form a diploid zygote Genes from the two chromosomes combine to determine the characteristics of that zygote The structure of a sperm cell allows it to be adapted to its function because: - It has a lot of mitochondria which supplies energy It has an acrosome releases enzymes that help digest (enter) the egg membrane Cell Division – Revision Pack (B3) PPQ(1): OCR Gateway January 2012 B1 B2 B3 PPQ(2): Cell Division – Revision Pack (B3) PPQ(3): Cell Division – Revision Pack (B3) Cell Division – Revision Pack (B3) PPQ(4): Cell Division – Revision Pack (B3) PPQ(5): PPQ(6): Cell Division – Revision Pack (B3) Mark Schemes: PPQ(1): PPQ(2): PPQ(3): PPQ(4): Cell Division – Revision Pack (B3) PPQ(5): PPQ(6):