* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Krebs Cycle
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
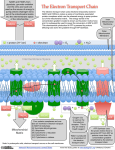
Mitochondrion Double membrane with intermembrane space Inner membrane folded into cristae; increase surface area Mitochondrion Gel-like matrix within inner membrane QuickTime™ and a Cinepak decompressor are needed to see this picture. Preparatory Reaction Pyruvate oxidized to acetyl CoA If O2 present, pyruvate enters mitochondrial matrix Preparatory Reaction Multienzyme complex: 1) Removes CO2 2) Oxidizes 2-C fragment + reducing NAD to NADH Preparatory Reaction 3) Attaches coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA Citric Acid Cycle Also called Krebs Cycle Catabolic process Completely oxidizes acetyl CoA to CO2 Citric Acid Cycle 8 enzyme catalyzed steps in mitochondrial matrix Citric Acid Cycle Acetyl CoA (2C) combines with oxaloacetate (4C) to become citrate (6C) Citric Acid Cycle ATP made by substrate level phosphorylation + NAD reduced to NADH FAD reduced to FADH2 Summary For each glucose molecule entering mitochondrion: 1) Two pyruvate oxidized to CO2 2) Coenzymes are reduced 8 NADH & 2 FADH2 produced Summary 3) 2 ATP produced by substrate level phosphorylation QuickTime™ and a Cinepak decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a Cinepak decompressor are needed to see this picture. ATP Production Most energy from glucose in NADH & FADH2 Electrons pass down the electron transport chain to oxygen Electron Transport Chain Electron carrier molecules embedded in inner mitochondrial membrane Electron Transport Chain Each one has higher electronegativity than previous one Electrons pulled downhill Electron Transport Chain Final electron acceptor is oxygen Most electronegative + O2 + 4e + 4H 2H2O Electron Transport Chain 3 protein complexes pump + H from matrix into intermembrane space Intermembrane space two pH units lower than matrix Proton Motive Force Energy stored in proton gradient across membrane Electrochemical gradient Chemiosmosis Couples ATP production with establishment of H+ gradient ATP Synthase Protons + (H ) diffuse down gradient through ATP synthase Causes oxidative phosphorylation of ADP ATP Production For each glucose: 2 net from glycolysis 2 from Krebs Cycle 32 to 34 from Electron Transport Chain ATP Production For each glucose: TOTAL 36 to 38 QuickTime™ and a Cinepak decompressor are needed to see this picture.