* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate Change - Harlem School District 122
Emissions trading wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Kyoto Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in New Zealand wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Climate Change conference wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
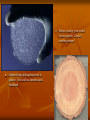
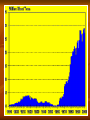
Climate Change History Climate has changed and shifted for millions of years Earth goes through warming and cooling phases How do they know?? Data from ice cores, radioisotopes in rocks and fossils, pollen, tree rings Gathered from drilling deep holes in glaciers. Sites such as Antarctica and Greenland. Shows a year by year record of trees growth. Can tell weather patterns. Greenhouse gases Include CO2, Methane, Nitrous oxide, CFC’s, and HFC’s (Hydrofluorocarbons) Fact – U.S. has 4.6% of the worlds pop. But produces ¼ of world CO2 emissions Reasons that back Global Warming 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The 20th century was the hottest in 1000 yrs Since 1861, temp. of Troposphere has risen .6Co 10 warmest years on record have occurred since 1990 Glacial melting is increasing Melting of permafrost in Alaska and Arctic Sea levels have rose 4-8 inches in the last century Factors effecting global climate 1. Oceans Currents act like a conveyor belt. They store CO2 and heat and is propelled by the wind. An increase or decrease in temp. will lead to a change in the currents direction. Disruption or slowing of the belt would cause drastic changes such as floods, drought, severe storms, and heat. 2. Outdoor pollutants Aerosols Produced by volcanoes and human activity Can warm or cool the air depending on their size and reflectivity 3. High levels of CO2 This would actually increase plant growth Which would decrease CO2 levels But all of the CO2 would be returned to the atmosphere when it dies 4. Increased Methane emissions A large release would come from permafrost melting This would warm the earth, which would then release more gas and so on. Options Three schools of thought 1. Wait and see strategy U.S. currently holds this policy 2. Act now to reduce the risks from climate change 3. Act now as part of a no-regrets strategy Prevention vs Cleanup Cut fossil fuels use Shift from coal to natural gas Shift to renewable energy Give this technology to developing countries Reduce deforestation Limit urban sprawl Slow population growth Scrub CO2 from emissions Store CO2 by planting trees Bury CO2 underground or deep in the oceans Repair leaky pipelines and facilities Use animal feed that reduces emissions by belching cows Kyoto Protocol December 1997, 161 nations met in Kyoto Japan to negotiate a treaty to help slow global warming Requires 39 developed countries to reduce greenhouse emissions by 2012 Why the 39? – they are the major polluters This did not require developing countries to lower their emissions until a later date U.S. withdrew from participating in the protocol in 2001 Why? China and India were not under the regulations Also, it was felt that it was too expensive Why is this difficult to deal with? 1. The problem has many complex causes. 2. The problem is global. 3. The problem is a long term issue 4. The harmful and beneficial impacts of climate change are not spread equally. 5. We cannot stop climate change, only slow and adapt to it. 6. Phasing out fossil fuels may disrupt economies and lifestyles. Good Karma? Great Britain -reduced its emissions to its 1990 levels. Mainly by improving energy efficiency in homes and industry China has reduced its CO2 emissions by 17% Conversely, the United States CO2 emissions rose by 14% Seed Vault Svalbard Global Seed Vault, also known as the doomsday Vault Dug into a mountain side in the Norway Will be used to hold large quantities of seeds from plants throughout the world Most importantly, seeds that make up most of the agricultural industry. No matter what, the seeds will be frozen