* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download final exam of medical immunology
Survey
Document related concepts
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
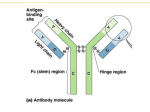
FINAL EXAM OF MEDICAL IMMUNOLOGY (A) NAME:_________________ Reg.NO:__________________Points_________________ Each of the following questions contains four suggested answers, choose the best one. 1Antibody can bind to A antigenic determinents C the whole antigen molecule B BCR D TCR 2Factors influence immunogenicity include A foreignness B molecular size C chemical composition D all above 3 Haptens are the molecules that A possess antigenicity C possess immunogenicity B are large protein D can induce the production of antibody 4 The first immunoglobulin class produced in a primary response to an antigen is A IgA B IgG C IgM D IgE 5 The most abundant immunoglobulin class in serum is A IgA B IgG C IgM D IgE 6 The Ig which serves an important effector function at mucous membrane surface is A IgA B IgG C IgM D IgE 7 The domains by which immunoglobulin bind to epitope are A constant region B variable region C framework region D hinge region 8 The monomer of IgM is composed of A two γheavy chains,and two κor two λlight chains. B two μheavy chains,and two κor two λlight chains. A two εheavy chains,and two κor two λlight chains. A two δheavy chains,and two κor two λlight chains. 9 Papain can digest the entire IgG into A two Fab fragment and one Fc fragment. A one Fab fragment and one Fc fragment. A two F(ab’)2 fragment and one Fc fragment. A one F(ab’) 2 fragment and pFc’. 10 C1q-binding site of IgM is located in A CH1 B CH2 C CH3 D CH4 11The most efficient Ig involved in the classical pathway of complement activation is A IgA B IgG C IgM D IgE 12 In the classical pathway of complement activation, C3 convertase is A C4b2a B C3bBb C C4b2a3b D C3bBb3b 13 The fragment that does not belong to the anaphylatoxin is A C3a B C3b C C4a C5a 1 14 The fragment involves in the opsonization is A C3a B C3b C C4a C5a 15 The regions that encode Class I HLA molecules are A locus A B locus B C locus C D all above 16 In Class I MHC molecules,peptide-binding site consist of A α1 and α2 domains B α1 and α3 domains C α1 and β1 domains D β2m 17 Biological role of the MHC proteins do not contribute to A A fundamental role in regulating immune responses. B Ag presentation C Self-MHC restriction. D Control of B cell development 18 The component which is capable of lysing microorganisms is A C1-9 B C5-9 C C3-5 D C8-9 19 In the classical pathway of complement activtion,the activation sequence is A C123456789 B C124536789 C C142356789 D C124356789 20Which property does not belong to cytokines A Pleiotropy B Redundancy C Synergy D Specificity 21 The formation of C3bBb can be inhibited by A DAF B factor I C factor H D all above 22 MBL activates the complement system via its ability to A directly cleave C4 Cdirectly cleave C2 B directly cleave C3 D bind to C1q 1. All of the following are true about neutrophils A. B. C. D. EXCEPT that… They have receptors for complement components and chemoattractive factors Are the main cells involve in acute inflammation Their granules involved in microbial killing Are the cells of the adaptive immune system 2. All of the following are true about macrophages EXCEPT… A. B. C. D. Settle mainly in the tissue. Can phagocyte microbes and dead body cells. Express CD14 Only involve in innate immunity 3. Opsonins include A. the complement component C3b and antibody B. MHC molecules C. Antigen D. Cytokines 4. Nature killer cells A. can kill virus infected cells by specific receptors recognization. B. Can secrete gamma interferon ( IFN ). 2 C. Can not be activated by IL-2. D. Do not express KAR and KIR. 5. All of the following are secondary lymphoid organs except… A. Spleen. B. Bone marrow. C. Lymph nodes. D. Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue . 6. All of the following are true about A. B. C. D. thymus Except… is the organ where T cell precursors mature. Provid positive selection and negative selection for T cells. Absence in new born mouse will cause T cell mediate immunity disorder. Absence in new born mouse will not affect B cell mediate immunity . 7. T cells do not… A. B. C. D. express CD3 produce cytokines to help other cell types. Mediate their functions by cell to cell contact. Recognize protein antigens without APC cells’ associated. 8. Th2 cells do not… A. B. C. D. express CD4. Produce IL-4,IL-10 et al. Involve in inflammatory . Help B cell activation. 9. Tc cells do not… A. express CD8. B. Mediate killing of virus infected cells . C. release lytic granules D. recognize antigens with MHC class II molecles. 10. All of the following are true about cell mediated immunity Except… A. Mediate by activated T cells and macrophages. B. Can be transferred by T cells. C. some times can cause delayed-type hypersensitivity. D.have no relationship with other cells. 11. T cell receptor (TCR) does not… A. provide T cell specificty. B. exist in a secreted form.. C. only recognize the MHC-antigen peptides complex. D.usually express /dimers. 12. All of the following are professional APC Except… 3 A. Mast cells. B. Macrophages. C. B cells. D. Dendritic cells. 13. The endogenous pathway of antigen presentation involves… A. presentation of antigen associated with MHC class II molecules. B. presentation of antigen to cytolytic T cells. C. presentation of antigen to Th2 cells. D. presentation of antigen to B cells. 14. All of the following are true about A. is an unsual immune response. B. is caused by antigen. hypersensitivity Except… C. is a primary immune response. D. can be classfied into four types. 15. The method that detects the antibody blocking the actions of a microorganism is: A. B. C. D. Agglutination Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay Neutralization Single radial immunodiffusion 16. In enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: A. Antibody or antigen is bound to an enzyme, which catalyzes the reaction. B. Substrates in the reaction is converted to a colored end-product. C. Antigen or antibody can be detected quantitatively with extremely sensitivity. D. All the above. 17. All of the following are involved in Immediate hypersensitivity except… A. mast cells B. IgE C. histamine D. platelets 18. Hemolytic disease of the newborn due to RhD incompatibility depends upon the… A. B. C. D. transplacental passage of anti-RhD IgG antibodies. transplacental passage of anti-RhD IgM antibodies production of cytoxic antibodies by the baby. The first pregnancy of the RhD+mother with RhD- fetus. 19. All of the following are true about immune-complex mediated type III hypersensitivity except A. B. C. D. immune-complex can be formed by serum products. Tissue damage can be caused by complement activation. Includes the Arthus reaction. Requires cytotoxic T cells. 4 20. All of the following are true about delayed-type hypersensitivity except… A. is mediated by T lymphocytes. B. includes contact sensitivity. C. includes the tuberculin reaction. D. includes Farmer’s lung. 21. Live vaccines are dangerous to the following people except… A. a pregnant woman. B. Teenagers. C. An immunologically incompetent host. D. Patients receiving immunosuppressive drugs. 22. Which of the following cell types is not involve in antibody production… A. Cytotoxic T cells. C. Th2 cells. B. B cells. D. Macrophages. 23. On the B cell surface, receptors for antigen are associated with… A. B5 molecules C. MHC class I molecules. B. Ig and Ig. D. MHC class II molecules. 24. All of the following are true about memory humoral immune response except… A. Usually produce more antibodies of IgG class B. The lag period is much shorter than the primary immune response. C. The affinity of antibodies is maturated. D. Produce IgM antibodies without class switching. 25. Stimulation of antigen-specific T cells by appropriately presented antigen alone results in… A. anergy. B. cell proliferation. C. production of various cytokines. D. release of perforin and granzymes. 26. B cells can express on their cell surface… A. membrane IgM and IgD stimultaneously. B. CD2 molecules. C. CD3 molecules. D. IgG that can bind several different unrelated antigens. 27. T lymphocytes can be activated by… A. specific antigen. C. Cytokines. B. Mitogen. D. All of the above. 28. Surface antigens on live cells can be identified by… A. ELISA. C. RIA B. FACS D. All of the above. 29. Both immune complex disease and delayed type hypersensitivity involve… A. IgG or IgM antibodies. 5 B. Complement. C. Phagocytic cells. D. B cells. 30. B cell activation can be modulated by the following molecules except… A. CD19. C. CD32. B. CD21. D. CD28. Answer sheet for multiple choice question 1. A B C D 6. A B C D 11. A B C D 16. A B C D 21. A B C D 26. A B C D 31. A B C D 36. A B C D 41. A B C D 46. A B C D 2. A B C D 7. A B C D 12. A B C D 17.A B C D 22. A B C D 27. A B C D 32. A B C D 37.A B C D 42. A B C D 47. A B C D NAME:_________________ 3. A B C D 8. A B C D 13. A B C D 18 A B C D 23.A B C D 28. A B C D 33. A B C D 38 A B C D 43.A B C D 48. A B C D 4. A B C D 9.A B C D 14. A B C D 19. A B C D 24. A B C D 29 A B C D 34. A B C D 39. A B C D 44. A B C D 49 A B C D 5. A B C D 10.A B C D 15. A B C D 20. A B C D 25. A B C D 30. A B C D 35. A B C D 40. A B C D 45. A B C D 50. A B C D Reg.NO:__________________ 6