* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells and Cell Theory
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
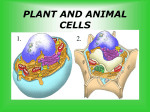
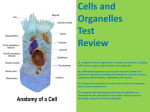
Cells and Cell Theory Organisms – living things All organisms are made up of cells. Multicellular: Examples: Unicellular: Examples: made of many cells Insects, snails, fish, people made of one cell bacteria, protists Exception: Viruses - Not alive - Made of proteins, not cells Organ system organ tissues cells organelles Organ - Group of different tissues that work together to do a certain job Organ Tissue system – a group of organs - Group of cells that look alike and work together to do a certain job Cell Theory (a scientific theory, not a law!) All living things or organisms are made of cells New cells are created by old cells dividing into two cells Cells are the basic building units of life Cells Basic unit of life The smallest living things First observed by Robert Hooke (1665-1703) A cell is like a factory with each “worker” having its own job. There are many types of cells, doing many different jobs in plants and animals. Types of Cells Eukaryotic Single Has cell a nucleus All organisms EXCEPT bacteria and archaea Prokaryotic Simplest No type of cell nucleus DNA and other materials float freely within the cytoplasm Bacteria and archaea Other Vocab Diffusion – Material moves from crowded area to less crowded area Homeostasis - Ability of organisms to maintain a state of balance Example: We maintain our body temperature by shivering to get warm and sweating to cool off. Organelle - Small structure inside a cell that performs a certain job Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) - system of tubes that move proteins within a cell Golgi Bodies - package and distribute (move) proteins outside the cell • Lysosome: digests waste, breaks down substances • Mitochondria: use oxygen to release energy, power supply Ribosome - Small round structure that makes proteins Meiosis Process of cell division Results in reproductive cells Mitosis Process of cell division Results in two cells Cells are identical to the parent cells Animal vs. Plant Cells Three Main Parts of Cells Cell Membrane 2. Nucleus 3. Cytoplasm 1. Cell Membrane Thin layer Encloses (surrounds) the cell Controls movement of materials into and out of the cell Provides shape to the cell Provides protection for the cell Nucleus Controls all cell activity Round or egg-shaped Found near the center of the cell Dark in color Contains DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid: chemical in chromosomes that stores information about the organism Cytoplasm Gel-like Contains all the living material except the nucleus Examples: Proteins Nutrients Organelles Plant cell parts Plant cells may contain some extra parts. Chloroplasts (plant cells) Chloroplasts which are disc shaped and contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis. Cell wall (plant cells) A cell wall which is a strong outer layer to support the cell and give it shape. Vacuole (plant cells) A vacuole where the plant cell stores sap (the food that it has made; a mixture of sugars, salts and water). To summarize: (draw and label this!)