* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introductory Psychology
Carolyn Sherif wikipedia , lookup
In-group favoritism wikipedia , lookup
Self-categorization theory wikipedia , lookup
Introspection illusion wikipedia , lookup
Implicit attitude wikipedia , lookup
Belongingness wikipedia , lookup
Social dilemma wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Group dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
Attribution bias wikipedia , lookup
Self-perception theory wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
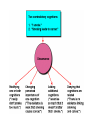
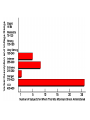
Social Psychology Social Thought Social Cognition The collection and assessment of information about other people Schemata Primacy effect Condition “Friendly” Ratings One-paragraph, friendly 95% One-paragraph, unfriendly 3% Two-paragraph, friendly-unfriendly 78% Two-paragraph, unfriendly-friendly 18% Social Thought Schemata Primacy effect Recency effect Stereotypes A set of characteristics presumed to be shared by all members of a social category Social Thought Attributions Internal/Dispositional External/Situational Kelley’s Covariation Model of Attribution Consensus Consistency Distinctiveness Attribution Errors Fundamental attribution error/Correspondence error tendency to explain others’ behavior in terms of dispositional (internal) rather than situational (external) causes Self-serving bias tendency to take credit for positive behavior or outcomes by attributing them to internal causes, but to blame negative ones on external causes, especially on factors beyond our control Attribution Errors Just World Hypothesis People Halo effect Good get what they deserve goes together… Assumed similarity bias Tendency to assume others are like self, even when meeting for first time Attitudes A relatively stable organization of beliefs, feelings, and behavior tendencies toward something or someone Can be positive or negative Affect behavior Attitudes Components of Attitudes Beliefs Feelings Behavior tendencies When Attitudes Go Bad… Prejudice Discrimination Belief negative stereotype Feelings strong, negative Behavioral Tendencies strong Sources of Prejudice Frustration-aggression theory Authoritarian personality Social conflict theory Social learning theory Information processing Stereotypes Persuasion Any attempt to change an attitude, and ultimately, behavior Source Message Medium Audience Cognitive Dissonance Discomfort experienced when there is an obvious gap between our attitudes and our actions or between two attitudes Boring Task (turning pegs) Explain to next subject that it was interesting Paid $1 Paid $20 “It was fun” = Attitude Change “It was boring” = NO Attitude Change Social Influence Attempts made by one or more people to change the attitudes or behavior of others Obedience A change of behavior in response to a command from an authority figure Stanley Milgram Relieved of personal responsibility Signs of authority Commands were gradual Conformity Voluntarily yielding to social norms, even at the expense of one’s own preferences Asch’s conformity studies 35% conformity rate Influential factors Situational characteristics Group size, unanimity Nature of the task Personal characteristics Compliance A change of behavior in response to an explicit request from another person or group Foot-in-the-door effect Door-in-the-face effect Lowball procedure That’s-not-all technique Not-so-free sample technique Social Action Bystander Effect Diffusion of Responsibility Mob behavior Deindividuation The more anonymous people feel in a group, the less responsible they feel as individuals