* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 OVERVIEW OF EXTRACELLULAR SIGNALING A. Steps of
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Ligand binding assay wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Ultrasensitivity wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
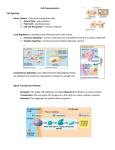
OVERVIEW OF EXTRACELLULAR SIGNALING A. Steps of extracellular communication 1. synthesis of signaling molecule 2. Release of signaling molecule 3. Transport of the signal to the target cell 4. Detection of the signal by a specific receptor protein 5. Change in cellular metabolism or gene expression triggered by the receptorsignaling molecue complex 6. Removal of the signal ==terminating the cellular response B. Types of Extracellular signaling 1. Endocrine 2. Paracrine 3. Autocrine 1 2 C. Receptor Proteins Exhibit Ligand-Binding Specificity and Effector Specificity 1. Lipophilic hormones with intracellular receptors a. steroids, thyroxine, retinoic acid 2. Water soluble hormones with cell-surface receptors a. peptide hormones; catecholamines 3. Lipophilic hormones with cell-surface receptors a. prostaglandins 3 4 5 D. Types of Cell Surface Receptors 1. G protein-linked 6 a. Trimeric Signal Transducing Gs Proteins link receptors with AC. 7 b. Gsα belongs to GTPase Superfamily of Intracelluar Switch Proteins 1. Ras 8 c. cycling of Gs between Active and Inactive forms 9 d. Effect of Bacterial toxins e. Amplification of Hormone signal f. Termination of Cellular Response 10 g. AC is Stimulated and Inhibited by Different Receptor-Ligand Complexes h. Multiple G proteins Transduce Signals from Seven-Spanning Receptors to Different Effector Proteins 11 12 13 2. Ion channel receptors a. Ach receptor 3. Receptors lacking intrinsic enzyme activity a. Cytokine receptors 4. Receptors with intrinsic activity a. Receptor Tyrosine Kinases 14