* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Autoimmune Disease
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
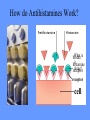
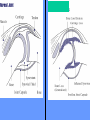
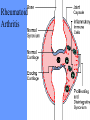
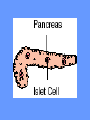
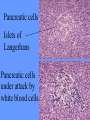
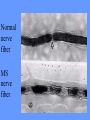
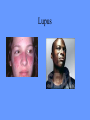
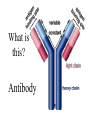
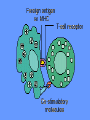
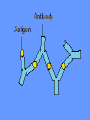
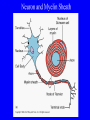
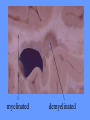
What is meant by “A case of mistaken identity”? Give an example. The Immune System Makes Mistakes attacks harmless foreign substances allergies attacks the body’s own tissues and organs autoimmune disease Allergies What are the symptoms of an allergic reaction? Allergy Symptoms What foreign substances cause allergies? Allergens – allergy-causing antigens Pollen Dust Mites Foods Animal Hair Allergy a rapid overreaction to an antigen (allergen) that is not normally harmful What is Histamines causing all these part of the inflammatorysymptoms? response released by cells stimulated by antigen (allergen) dilates blood vessels increases the permeability of the capillaries to white blood cells and some proteins allows them to engage pathogens in the infected tissues Histamines How do Antihistamines Work? What is blocks it histamine doing? receptor receptor cell Autoimmune Disease • condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own organs and tissues Autoimmune Diseases • juvenile diabetes • rheumatoid arthritis • multiple sclerosis (MS) • lupus • rheumatic fever Why would the body attack itself? What is the mistake made by the immune system? Hint: In order for the immune system to be successful in defending the body, what two things must it be able to distinguish? The basis of immunity is in the body’s ability to distinguish between its own substances (“itself”) and foreign substances (“nonself”) “Self molecules” (“I.D. tags”) Autoimmune Disease immune system fails to recognize some of the body’s tissues as “self” - Like a “case of mistaken identity” Why does this happen? Hypothetical Factors Influencing Autoimmune Disease • infections • aging • chronic stress • hormones Rheumatic fever • caused by a bacteria (strep) • triggers an immune response against heart and joint tissues individual produces antibodies to antigens of strep bacteria strep antigens are structurally similar to antigens of the heart anti-strep antibodies attack sites on the heart, damage the heart muscle and heart valves. Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis White blood cell attack leads to the destruction of cartilage and bone in the joint Rheumatoid Arthritis white blood cells attack cells inside joint capsule producing inflammation inflammation causes cells of capsule to grow and divide abnormally abnormal cells destroy cartilage and bone in the joint Pancreatic cells Islets of Langerhans Pancreatic cells under attack by white blood cells Juvenile Diabetes (Type I diabetes mellitus) Antibodies destroy insulin-producing cells of pancreas Normal nerve fiber MS nerve fiber Multiple Sclerosis (MS) • White blood cells attack and damage nerve cells • Damage interferes with messages between nerves and the body Lupus Lupus antibodies attack nucleic acids and cell organelles such as ribosomes and mitochondria Lupus • virus might trigger the disease in genetically susceptible individuals • inflammation and damage to various body tissues joints, skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, blood vessels, brain Vaccine – a weakened or dead pathogen put into the body to stimulate the production of antibodies and the primary immune response How might a vaccine induce an autoimmune disease? antigen similar to substance in body? Treating Autoimmune Disease immunosuppressive drugs and steroids Problems • infections • not specific Autoimmunity vs. Immunodeficiency What is this? Antibody Active Immunity Passive Immunity You make the antibodies You don’t make the antibodies Exposure to antigen - injection - vaccine - infection - breastfeeding In some cultures it is normal for babies to be breast-fed for up to 4 years! Benefits of Breastfeeding Breast milk: http://www.webmd.com • provides ideal nutrients for infants (vitamins, protein, and fat) in a form more easily digested than infant formula • contains antibodies that help your baby fight off viruses and bacteria • lowers the baby's risk of having asthma or allergies • babies who are breastfed exclusively for the first 6 months, without any formula, have fewer infections (ear infections, respiratory illnesses, bouts of diarrhea, hospitalizations and trips to the doctor.) Benefits of Breastfeeding • Breastfeeding has been linked to higher IQ scores in later childhood in some studies. • Physical closeness, skin-to-skin touching, and eye contact all help baby bond with mother • Infants are more likely to gain the right amount of weight as they grow rather than become overweight children. • May also plays a role in the prevention of SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome). • May lower the risk of diabetes, obesity, and cancer Benefits of Breastfeeding Breastfeeding: • burns extra calories, so it can help mom lose pregnancy weight faster. • releases the hormone oxytocin, which helps the mother’s uterus return to its pre-pregnancy size and may reduce uterine bleeding after birth. • lowers mother’s risk of breast and ovarian cancer. • may lower mother’s risk of osteoporosis • saves time and money (you don't have to buy and measure formula, sterilize nipples, or warm bottles) Active immunity Passive Immunity When the boy got infected the first time his primary immune response was activated and he made antibodies to attack the antigen. His immune cells divided and left behind memory cells. When he got infected the second time his memory cells made the secondary immune response fight the disease faster and stronger, so he didn’t even get sick. myelinated demyelinated Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Myelin protein surrounding nerve cells is attacked and destroyed nerve impulses are slowed or blocked Rheumatic fever • can occur following untreated streptococcus (strep) infection • most often affects children causing painful, inflamed joints • in some cases, permanent damage to heart valves.