* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mr. Haan`s Science
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Sexual dimorphism wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Sex-limited genes wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
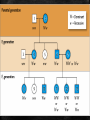
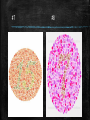
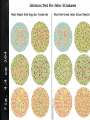
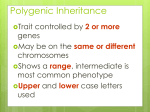
Extending Mendelian Genetics Chapter 7 page 186 A. Chromosomes and Phenotype 1. 2 copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype a. Inherit 1 set of chromosomes from each parent b. Homologous chromosomes could have same gene but different alleles c. Gene expression often related to whether the gene is on an autosome or sex chromosome d. Disorders caused by recessive alleles 1) Only homozygous recessive individuals express the disorder 2) Carrier – does not show symptoms but can pass on the disease 3) Parents are typically heterozygous for the trait 4) Ex – Cystic fibrosis Punnett Square for Cystic Fibrosis e. Disorders caused by dominant alleles 1) Less common than recessive disorders 2) At least one parent will have the disorder 3) Huntington’s disease 2. Sex-linked traits a. Sex-linked genes 1) Genes located on the sex chromosomes 2) XX genotype = female and XY genotype = male 3) Females can only give an X, males can give an X or Y 4) Genes on X and Y chromosomes are sex-linked 5) X chromosome carries nearly 1100 genes, but the Y chromosome has less than 250 6) More traits are controlled by the X chromosome b. Expression of sex-linked genes 1) Sex linked traits are more common in males a) Males only have 1 X chromosome b) One recessive trait on an X chromosome gives an expressed trait 2) Females a) X chromosome inactivation – 1 X chromosome is randomly turned off Female b) Causes a “patch work” of different genes in cells c) Female calico and tortoiseshell cats Male B. Complex Patterns of Inheritance 1. Incomplete Dominance a. Heterozygous phenotype is b/w the two homozygous phenotypes b. Neither is completely dominant or recessive c. Beta fish and snap-dragon Incomplete dominance Green (B1B1) Steel Blue (B2B2) Royal Blue (B1B2) 2. Codominance a. Both traits are expressed equally b. Red flowers x white flowers = red and white patches c. Blood type 1) A and B alleles are codominant 2) O allele is recessive 3) A and B blood means you make proteins called antigens Human Blood Types 3. Polygenic Traits a. Traits produced by two or more genes b. Skin, eye, and fur color c. Green dominant over blue yet recessive to brown d. Epistatic gene 1) Interferes with all other gene expression 2) Can cause albinism 4. Environmental influence a. Gender of turtles before hatching 1) Warm temperatures = females 2) Cooler temperatures = males b. Genotypes may express different phenotypes 1) Hair changes color in summer from the sun 2) Artic fox has white fur in winter and brown in summer c. Identical twins raised in different environments 29˚ C = 84.2˚ F Arctic Fox Summer Winter C. Human Genetics and Pedigrees 1. Studying genetics of simple organisms helps us understand our genetics 2. Genetics are the same in all sexually reproducing organisms 3. Inheritance of many human traits is very complex 4. Females can carry sex-linked disorders a. Males only have 1 X chromosome 1) They express every X-linked trait (dominant or recessive) 2) Nothing to mask recessive traits 3) Males can’t be carriers of sex-linked traits only females b. Expression of disorder depends on: 1) Which parent carries the allele 2) Sex of the child c. Ex: Hemophilia and color blindness 5. Pedigrees a. Chart which traces geno/phenotypes in a family to determine if people are carriers b. Used by genetic counselors to determine probability of parents having children with genetic disorders c. Determining autosomal trait or sex-linked: 1) Sex-linked – appear more often with males 2) Autosomal – appear equally b/w both males and females d. Key 1) Boxes – males 2) Circles – females 3) Shaded – person expresses trait 4) Half shaded – person is a carrier 5) Line through it – person has died 6) Connecting lines – shows mate or children Colorblindness Colorblindness Test #3 #4 #5 #6 #7 #8 Fig. 4.4 pg 204 6. Karyotypes a. Genome – all DNA in a cell b. Karyotype – picture of all chromosomes in a cell c. Used to detect large changes like #, size, or shape of chromosomes d. Human Genome Project 1) International effort 2) Tries to map, sequence, and ID all genes in human genome Human Karyotype Is this karyotype from a male or female?