* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT 2 CELLS AND SYSTEMS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
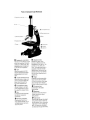
UNIT 2 CELLS AND SYSTEMS TOPIC 1 LIVING ORGANISMS FUNCTIONS TO STAY ALIVE: LIVING ORGANISMS NEED ENERGY LIVING ORGANISMS RESPOND AND ADAPT TO THEIR ENVIROMENT LIVING ORGANISMS REPRODUCE LIVING ORGANISMS GROW LIVING ORGANISMS PRODUCE WASTES CELL: basic unit of every system TOPIC 2 MICROSCOPES AND CELLS ANTON VVAN LEEUWENHOEK- invented microscope, first person to observe organisms made of only one cell single celled organisms called “animalcules” ROBERT HOOKE- described little boxes as cellulae, meaning “little rooms” first to give use present day word “cell” MATTHIAS SCHLEIDEN AND THEODORE SCHWANN- hypothesis that all organisms are composed of cells (the cell is the basic unit of life) RUDOLF VIRCHOW- contributed his ideas to Schleiden and Schwann about cell theory -All living things are composed of one or more cells - Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms MAGNIFYING: makes object appear larger MICROSCOPES: instruments that magnify objects JAMES HILLIER AND ALBERT PREBUS- invented electron scanning microscope HOW TO CALCULATE THE FIELD OF VIEW Medium-power Field of view = low-power field of view MULTICELLULAR- many celled organism UNICELLULAR- single-celled organism ORGANELLES- structure inside the cell = magnification of low-power objective lens Magnification of mediumPower objective lens TOPIC 4 FLUID MOVEMENT IN CELLS SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE- allows only certain materials to cross it PERMEABLE- lets all materials cross it IMPERMEABLE- lets nothing cross it DIFFUSION- the movement of particles in liquids and gases from an area of higher concentration to and area of lower concentration (spreading out process) OSMOSIS- the diffusion of a solvent through a selectively permeable membrane VASCULAR TISSUES- tissues found in plants that connect the roots to the leaves PHLOEM TISSUE- transports sugars manufactured in the leaves to the rest of the plant XYLEM TISSUE- conducts water and minerals absorbed by the root cells to every cell in the plant ROOT HAIR- on a plant root, an extension of a single epidermal cell. Water enters a root hair by osmosis TRANSPIRATION- loss of water from a plant through evaporation TOPIC 5 CELL SPECIALIZATION AND ORGANIZATION SPECIALIZED- in living things having different appearances and able to perform different tasks TISSUES- groups of cells having the same structure and function ex. Skin, nerve, muscle ORGANS- group of tissues that work together to perform a function ex heart SYSTEMS- organs work together to form system TOPIC 6 BODY SYSTEMS IN HUMANS DIGESTIVE SYSTEM RESPIRATORY SYSTEM CIRCULATORY SYSTEM MAJOR BODY SYSTEMS DIGESTIVE- breaks down food, absorbs food particles and eliminates wastes. RESPIRATORY- exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide CIRCULATORY- circulates blood, transports food particles, dissolved gases, and other materials NERVOUS- controls and co-ordinates body activities. Senses internal and external changes EXCRETORY SYSTEM-main function to filter waste materials from the blood key organs are the kidneys TOPIC 7 BODY SYSTEMS AND YOUR HEALTH BLOOD COMPONENTS AND THEIR FUNCTION PLASMA RED BLOOD CELLS 44% 55% carries nutrients, waste products hormones, and blood cells carry oxygen WHITE BLOOD CELLS less than 1% defend body against infection and disease cause blood to clot (thicken) at site PLATELETS less than 1% wounds to prevent blood loss Blood pressure indicates several things about the health of the circulatory system for example volume of blood, heart rate, artery size, artery elasticity, blood viscosity. FOOD provides NUTRIENTS in the form of CARBOHYDRATE, FATS, PROTEINS, VITAMINS, MINERALS AND WATER which provide ENERGY AND MATERIALS used for GROWTH, DEVELOPMENT, AND REPAIR