* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Indicators and Effects of Climate Change File
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Snowball Earth wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
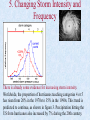
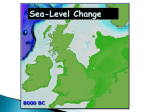
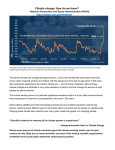
Indicators and Effects of Climate Change Indicators of Climate Change There are several indicators that help us to perceive changes in global climates. •global warming •changes in polar and glacial ice •rising sea levels and increasing Indicators ocean acidity of Climate •changing wind and precipitation patterns Change •changing storm intensity and frequency Effects – All of the above lead to changes in biomes 1. Global Warming The average global temperature is rising Not convinced? Click on the above picture to link to some “scientific” evidence. 2. Changes in Polar and Glacial Ice Generally, rising global temperatures have been associated with a decrease in the extent of coverage of the earth’s oceans by sea ice. Changes in Polar and Glacial Ice Satellite images taken at the same time of year clearly indicate a decline in the arctic polar ice cap in recent decades. Changes in Polar and Glacial Ice Sea ice thickness has likewise shown substantial decline in recent decades. Using data from submarine cruises, scientists have determined that the mean ice draft at the end of the melt season in the Arctic has decreased by about 1.3 meters between the 1950s and the 1990s. Changes in Polar and Glacial Ice Canadian glaciers have been melting rapidly since the end of the Little Ice Age about 150 years ago. Continuing climate changes, which are predicted to result from increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, are likely to have a further and significant impact on the glaciers in Canada. Continued glacier shrinkage would contribute to global sea level rise, and increased inputs of fresh water to high latitude oceans might modify ocean currents in the North Atlantic. Some glaciers will ultimately disappear. 3. Rising Sea Levels In the past 100 years, sea levels on earth have risen 10-15 cm. This effect has been attributed to a combination of melting ice and thermal expansion as the temperature of the sea-water has increased as well. Coastal areas become much more vulnerable to storms and flooding when sea levels are increased. 4. Ocean Acidity As the result of increased levels of carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere, there has been a drop in the surface ocean pH due to increasing acidity levels in the sea water. More CO2(g) leads to a lower pH by driving the following chemical reaction forward. CO2(g) + H2O H2CO3(aq) carbonic acid Rising acidity affects coral reefs which exhibit great amounts of biodiversity. The coral becomes “bleached” in the more acidic environment. The fishing industry may also be affected in the long run. 5. Changing Storm Intensity and Frequency There is already some evidence for increasing storm intensity. Worldwide, the proportion of hurricanes reaching categories 4 or 5 has risen from 20% in the 1970s to 35% in the 1990s. This trend is predicted to continue, as shown in figure 3. Precipitation hitting the US from hurricanes also increased by 7% during the 20th century. 6. Changing Wind and Precipitation Patterns The speed, frequency, and direction of winds have fluctuated unpredictably for several years. Increased temperature can also influence precipitation patterns. According to the above model, where will it get drier over the next several decades? Where will it get wetter? Effects of Climate Change As earth’s climate changes, there will be changes in the distribution of energy over the earth’s surface. This will lead to changes in wind speed, wind direction, and patterns of precipitation. Climate changes can lead to changing biomes which in turn could lead to widespread extinction of various species through: •desertification •shrinking wetlands •deforestation Changing Biomes While many species could become extinct due to rapid climate shifts, other species may flourish and could move into regions where they were otherwise unknown. These invasive species could put even more pressure on native species and may also introduce diseases that affect humans. Eg. West Nile virus, and waterborne diseases such as Yellow Fever. See Figure 7.27 p.297 ON Science 10, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Review Questions p.299 #1 to 8