* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
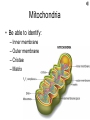
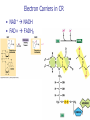
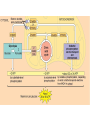
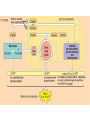
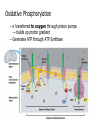
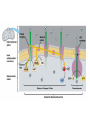
Big Idea/Question…. • How is life as we know it powered? • PS • CR Unit 4 Part 5 Cellular Respiration: Inputs, Outputs & mitochondria Learning Targets 5. Identify the inputs and outputs and location of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. 7. Compare and contrast the structure and function of mitochondria and chloroplasts. Cellular Respiration Location? Mitochondria • Be able to identify: – Inner membrane – Outer membrane – Cristae – Matrix Cellular Respiration • What is it? – Converts potential chemical (glucose) energy into ATP – 1 glucose can produce somewhere around 34 ATP molecules!! • Who does it? – Plants, animals and some bacteria • How?..... Cellular respiration • The process: • Reactants (inputs): Glucose & Oxygen • Products (Outputs): CO2, H2O & ATP Learning Check • What are some similarities between mitochondria and chloroplasts? • Where does Cellular respiration occur? • What are the inputs for CR? • What are the outputs for CR? Unit 4 Cell Energetics Part 6 Glycolysis, Bridging Process, the Krebs Cycle/Citric Acid Cycle & Oxidative phosphorylation Learning Targets 5. Identify the inputs and outputs and location of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Electron Carriers in CR • NAD+ NADH • FAD+ FADH2 Cellular Respiration • • • • Glycolysis Bridging Process Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain Glycolysis • • • • • Glycolysis splitting glucose Location cytoplasm Anaerobic (no O2 required) Utilized by ALL cells Steps – Energy Investment – Energy Payoff • Per Glucose – Produces 2 ATP ( 5 % of available energy) – 2 NADH – 2 Pyruvate Glycolysis Animation http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/ chapter25/animation__how_glycolysis_wo rks.html Now what?? Bridging (Transition) Process • Aerobic requires O2 as final electron acceptor (happens in ETC) • Location --inside mitochondria “One-Two Punch” – Carbonyl group released as CO2 – NAD+ reduced to NADH – Leaves Acetyl--picked up by CoA & becomes Acetyl CoA • Surplus of ATP acetyl-CoA gets stored as lipid • Little ATP acetyl-CoA enters Krebs cycle & makes ATP Krebs Cycle aka Citric Acid Cycle • Location--Matrix of mitochondria • Aerobic requires O2 as final eacceptor • Produces: – – – – CO2 (from carbonyl) NADH FADH2 ATP Electron Transport Chain • Location--Membrane of cristae • Aerobic requires O2 (final electron acceptor) • Follow the electrons—and protons! • Animation – vcell.ndsu.nodak.edu/animations/etc/first.htm Oxidative Phosphorylation • Electrons power proton pumps (which are imbedded proteins) pump H+ into intermembrane space (ETC) • Generates ATP when H+ diffuse back into matrix thru ATP Synthase (Chemiosmosis) • NAD+ powers 3 pumps 3 ATP • FAD+ powers 2 pumps 2 ATP • http://www.nature.com/nrg/journal/v2/n5/animation/nrg0501_342a_swf_MEDIA1.html Oxidative Phosphorylation – e- transferred to oxygen through proton pumps builds up proton gradient – Generates ATP through ATP Synthase Learning Checks • What are the 4 parts of Cellular Respiration, and where are they located? • Mitochondria transfer _____________ energy from ________ to ATP; chloroplasts transform ___________energy into the chemical energy.