* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
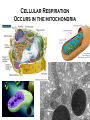
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
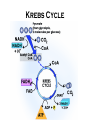
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
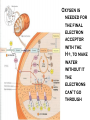
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Process cells use to harvest energy from organic compounds and convert it into ATP Breakdown of Glucose C6H12O6 +6O2 6CO2 +6H2O +ATP Oxygen makes process more efficient Aerobic – process that requires oxygen Anaerobic – process that does not require oxygen Cellular Respiration Occurs in the mitochondria Stage 1 Glycolysis Glucose (6 Carbon molecule) is converted into 2 pyruvate (3 Carbon molecule) and 2 ATP and NADH (Electron carrier) through a process called glycolysis Glycolysis OCCURS IN CYTOPLASM 1 6 Carbon molecule 2 3 Carbon Pyruvate ions 2 ATP molecules NAD+ (Electron carrier) – carries electron as NADH and in order for Cellular Respiration to continue NADH must donate electron elsewhere so NAD+ can recycle This last part is huge Stage 2 Aerobic – Occurs in mitochondria of eukaryote or cell membrane of prokaryote and can produce up to 36 ATP Anaerobic – Glycolysis – pyruvate – lactate or ethanol and CO2 Aerobic Pyruvate enters mitochondria A. Krebs Cycle – Pyruvate enters the mitochondria. enzyme assisted Rx producing ATP, NADH, FADH2 and starts again, CO2 is released during the Krebs cycle Stealing Electrons to give to the Electron Transport chain B. Electron Transport Chain NADH donates E to chain, protein pumps H+ out producing concentration gradient, H+ diffuses back in giving off energy to add P to ADP, O2, H+ and E to make water Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain Oxygen is needed for the final electron acceptor with the H+, to make water without it the electrons can’t go through Anaerobic Occurs because O2 is not present to accept the electron to form water at the end of the chain so the electron is not transferred from NADH and NAD+ cannot be recycled Fermentation process of recycling NAD+ to an organic H+ acceptor and just allows glycolysis to occur again Lactic Acid Pyruvate is converted into Lactate in order for glycolysis to continue. If lactate builds up and is not removed quickly enough, this may cause muscle soreness. Alcohol fermentation Carried out by yeast and fungus to produce beer, wine, milk, cheese, bread etc. Pyruvate is broken down into Ethanol which releases CO2 which allows glycolysis to continue. Pyruvate - Lactate (Lactic Acid) Pyruvate - Ethanol and CO2 Bread, Beer, Wine