* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
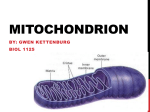
2.5 D: Cellular Respiration Quiz 1. The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The diagram below shows the movement of ions in the electron transport chain within a mitochondrion. Which statement best describes the movement of ions shown in the diagram? (A) The electron transport chain is used to move hydrogen ions to the inner membrane space, where they create a highly reducing environment and hydrolyze CO2 to produce sugar. (B) Hydrogen ions diffuse into the inner membrane space and are pumped against an electrochemical gradient through the electron transport chain, which provides the energy needed to generate ATP through chemiosmosis. (C) The proteins in the electron transport chain create an electrochemical gradient by pumping hydrogen ions to an area of high concentration, which powers ATP production when the hydrogen ions diffuse back into the mitochondrial matrix. (D) Hydrogen ions are reduced as they move through the electron transport chain in order to transfer electrons to ADP and phosphate to make ATP in the inner membrane space. Page 1 of 5 2.5 D: Cellular Respiration Quiz 2. A certain drug greatly disrupts cellular respiration. When the drug is introduced into the body, the following observations are made: • Acetyl CoA builds up in the mitochondrial matrix; • There is a decrease in the amount of CO2 diffusing out of the mitochondria; and • Low levels of NADH and FADH2 slow oxidative phosphorylation on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Which statement best explains how this drug disrupts cellular respiration? (A) The drug prevents the movement of hydrogen ions into the inner membrane space, which prevents the formation of an electrochemical gradient. (B) The drug prevents enzymes from splitting glucose into pyruvic acid during glycolysis and prevents the production of ATP during substrate-level phosphorylation. (C) The drug prevents the reduction of NAD+ and FAD by binding to the enzymes involved in the citric acid (Krebs) cycle. (D) The drug prevents the oxidation of NADH and FADH2 by blocking proteins from donating or accepting electrons in the electron transport chain. Page 2 of 5 2.5 D: Cellular Respiration Quiz 3. The diagram below shows the processes occurring in and around the inner mitochondrial membrane. Based on the diagram, which question best investigates a factor that affects the processes? (A) If water is generated in the mitochondrial matrix, will the mitochondrial matrix become hypotonic to the intermembrane space as the processes occur? (B) If oxygen gas is being converted into water in the mitochondrial matrix, will the volume of the mitochondrial matrix change as the processes occur? (C) What effect will lowering the pH in the intermembrane space have on the proteins in the inner mitochondrial membrane? (D) What effect will the movement of negatively charged ions through the inner mitochondrial membrane have on the production of water? Page 3 of 5 2.5 D: Cellular Respiration Quiz 4. A root cutting is placed in a sealed container. The concentrations of carbon dioxide and oxygen gas in the container are measured and recorded in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) every 6 hours over the next 24 hours. The results are shown in the table below. Which statement best explains the results of the experiment? (A) The root cutting is undergoing anaerobic fermentation because the root cutting is running out of oxygen and it is not able to undergo the citric acid cycle or oxidative phosphorylation. (B) The root cutting is using the Calvin cycle to generate energy and is consuming oxygen because there is not enough light available to carry out light reactions. (C) The root cutting is undergoing aerobic cellular respiration because the root cutting is generating carbon dioxide from organic molecules and is reducing oxygen to form water. (D) The root cutting is undergoing photolysis in the light-dependent reactions because oxygen is being split and combined with carbon to form carbon dioxide. Page 4 of 5 2.5 D: Cellular Respiration Quiz 5. The diagram below shows how the nutrients triglycerides, glucose, and amino acids are metabolized to produce ATP in a mitochondrion. Which scientific question is most appropriate to investigate the process of ATP production that is shown in the diagram? (A) How does the amount of ATP generation vary among each of the nutrients when oxygen supplies are limited? (B) How is the production of fatty acids in the cytosol affected by an excess supply of each nutrient? (C) How does the Krebs cycle vary based on the nutrient being metabolized? (D) How does NAD+ and FAD oxidation vary for each of the nutrients? Page 5 of 5