* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mitochondrion 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
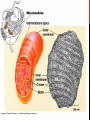
MITOCHONDRION BY: GWEN KETTENBURG BIOL 1125 STRUCTURAL BASICS • Sausage shaped organelles the size of bacteria • Bounded by two membranes • Smooth outer membrane • Inner folded membrane called cristae • Two compartments with free space • Matrix – Inside inner membrane • Ribosomes found here • Mitochondrial DNA • Intermembrane space – Lies between the two mitochondrial membranes FUNCTIONAL BASICS • “Powerhouse of the cell” • Main function is to produce energy in the form of ATP • Adenosine Triphosphate • Formed by metabolizing sugar • Cellular respiration • Oxidative metabolism • Proteins on inner membrane carry out this process CELLULAR RESPIRATION OTHER FUNCTIONS • Help maintain proper concentration of calcium ions within the cellular compartments • Play an important role in programmed cell death (apoptosis) MITOCHONDRIAL DNA (MDNA) • Located in the matrix • Helps the mitochondria divide independently from the cell • Contains 37 genes • mDNA is maternally passed down to a mother’s offspring • Mutations in mDNA can lead to many illnesses such as exercise intolerance MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASE • Does most damage to the cells of the brain, heart, liver, skeletal muscles, kidney, and the endocrine and respiratory systems • Result of inherited or spontaneous mutations in the mitochondrial DNA • Symptoms can include loss of motor control, muscle weakness and pain, poor growth, diabetes, lactic acidosis, developmental delays, and susceptibility to infection OTHER DISEASES LINKED TO DISFUNCTIONAL MITOCHONDRIA • Alzheimer’s dementia • Parkinson’s disease • Huntington disease • Diabetes