* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendelian Genetics
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
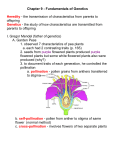
Unit 5 Notes: Mendelian Genetics Name:_________________________________________ Date: ___________ Genetics: the branch of biology that studies heredity Heredity: Is the passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring Trait: A characteristic coded for by a gene. ˃ Height (tall or short) ˃ Color (purple or white) ˃ Shape (smooth or wrinkled) Inherited traits: Characteristics that are inherited or passed on from parents to offspring Acquired traits: characteristics that you get as you go through life (not inherited) Gregor Mendel: the father of genetics. ˃ Mendelian Genetics ˃ He worked with garden pea inheritance in the 1800’s. ˃ His ideas were not accepted widely until the 1900’s Scar Law of Segregation ˃States that every individual has two alleles of each gene and when gametes are produced, each gamete receives one of these alleles Pollination: (plants)Is the transfer of pollen from anther (male) to stigma (female) Gamete: Sex cell (sperm or egg) produced by an organism ˃ The sperm in the pollen grain fertilizes the egg in the female part of the flower (pistil) Zygote: A fertilized egg; formed when a sperm unites with an egg. Self Pollination: The transfer of pollen from anther to stigma on the same flower Cross Pollination: The transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma on a different flower Chromosome: Dark rod-shaped bodies (coiled up chromatin) inside a cell’s nucleus made of DNA Unit 5 Notes: Mendelian Genetics Name:_________________________________________ Date: ___________ Gene: A segment of DNA on a chromosome that directs protein production for a trait ˃ located on the chromosome ˃ exist in alternative forms Allele: alternate forms of a gene Monohybrid: Crosses that involve only 1 trait Monohybrid cross » P1 = original parents --- grandparents » P1 x P1 = F1 (F = offspring) --- parents »F1 x F1 = F2 --- you Rule of Dominance Dominant allele: a gene that expresses itself in the presence of a weaker form of the gene (capital letter- example T = tall) Recessive allele: a gene that is masked in the presence of a dominant allele (lowercase letter –example t = short) Phenotype: the way an organism looks & behaves. Genotype: the alleles (letters) that determine how an organism looks or behaves. Homozygous: purebred; having 2 identical alleles ˃ TT – homozygous dominant ˃ tt – homozygous recessive Heterozygous: hybrid; having 2 different alleles > Tt – heterozygous dominant Punnett Square: Shorthand way of finding the expected proportions of possible genotypes in the offspring of a cross. > Devised by Reginald Punnett in 1905 Unit 5 Notes: Mendelian Genetics Name:_________________________________________ Date: ___________ Probability: The chance that an event will occur ˃ Determined by dividing the desired outcomes by the total number of possible outcomes ˃ Expressed as a fraction or a percent T t Cross a heterozygous tall plant with a heterozygous tall parent. Tt x Tt T (T= tall) (t=short) » » Genotypic ratio: 1:2:1 Phenotypic ratio: 3:1 t Cross a homozygous tall plant with a short plant. TT x tt » » T T TT T t Genotypic ratio: 4:0 Phenotypic ratio: 4:0 t Cross a plant that is pure tall with a plant that is heterozygous tall. TT x Tt » » T TTT T Genotypic ratio: 2:2 Phenotypic ratio: 4:0 t Independent Assortment » States that the genes for different traits are inherited independently of each other. Dihybrid cross: involve two traits » RrYy X RrYy RY Ry rY ry » Genotypic ratio: 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1 Phenotypic ratio: 9:3:3:1 RY RRYY RRYy RrYY RrYy Ry RRYy RRyy RrYy Rryy rY RrYY RrYy rrYY rrYy ry RrYy Rryy rrYy rryy Unit 5 Notes: Mendelian Genetics Name:_________________________________________ Date: ___________ Cross a cat heterozygous for both traits with a cat homozygous recessive for both traits. HhTt x hhtt » Genotypic ratio: 4:4:4:4 Phenotypic ratio: 4:4:4:4 ht ht ht ht HT HhTh HhTh HhTh HhTh Ht Hhtt Hhtt Hhtt Hhtt hT hhTt hhTt hhTt hhTt ht hhtt hhtt hhtt hhtt