* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics - walker2016
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
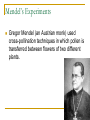
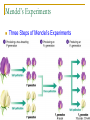
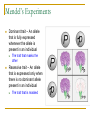
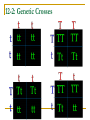
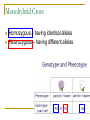
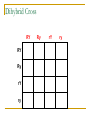
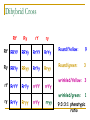
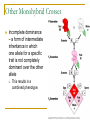
Genetics Chapter 12 12-1: Origins of Hereditary Science Mendel’s Experiments Genetics – The study of how characteristics are transmitted from parents to offspring Heredity – The passing on of genetic characteristics from one generation to another Mendel’s Experiments Gregor Mendel (an Austrian monk) used cross-pollination techniques in which pollen is transferred between flowers of two different plants. Mendel’s Experiments Reasons Mendel used pea plants Require little care Produce many offspring Mature quickly (8-10 weeks) Mendel’s Experiments P (parental) generation – Organisms that are true-bred for specific traits F1 generation – Offspring of the P generation F2 generation – Offspring of the F1 generation F = Filial (pertainting to a son or daughter) Mendel’s Experiments Self-pollination – A plant with both male and female reproductive organs that fertilizes itself Cross-pollination – Pollen from one plant is carried to the flower of another plant Mendel’s Experiments Three Steps of Mendel’s Experiments Mendel’s Experiments Gene – A section of DNA that carries the information on how to make one protein Mendel’s Experiments Allele – An alternative form of a gene One allele for each trait is passed from each parent to the offspring. Mendel’s Experiments Dominant trait – An allele that is fully expressed whenever the allele is present in an individual The trait that masks the other Recessive trait – An allele that is expressed only when there is no dominant allele present in an individual The trait that is masked 12-2: Genetic Crosses Monohybrid Cross Monohybrid cross – A cross in which one characteristic is tracked Punnett square – used to predict the outcome of genetic crosses Monohybrid Cross Genotype – the genetic makeup of an organism (use letters) Phenotype – the appearance of an organism (physical appearance) Monohybrid Cross Homozygous – having identical alleles Heterozygous – having different alleles Monohybrid Cross Trait – Plant height Phenotype T – tall t – short Genotype TT – homozygous dominant (pure bred) Tt – heterozygous (hybrid) tt – homozygous recessive (pure bred) Monohybrid Cross Probability – the likelihood that a specific event will occur Probability = number of one kind of possible outcome total number of all possible outcomes A probability may be expressed as a decimal, a percentage, or a fraction Mendel’s Characteristics Monohybrid Cross Ratios and percentages TT x tt = 100% heterozygous TT x TT = 100% homozygous dominant tt x tt = 100% homozygous recessive Tt x tt 50% heterozygous 50% homozygous recessive Monohybrid Cross Ratios and percentages Tt x Tt = Genotypic ratio – 1:2:1 ratio 25% homozygous dominant 50% heterozygous 25% homozygous recessive Tt x Tt = Phenotypic ratio – 3:1 75% tall 25% short Dihybrid Cross Dihybrid cross – A breeding experiment that tracks the inheritance of two traits Example Traits: Pea shape & Pea color Alleles: R – round r – wrinkled Y – yellow y – green Dihybrid Cross Use the FOIL method for each parent to setup the Punnett square RrYy x RrYy RY Ry rY ry RY Ry rY ry Dihybrid Cross RY RY Ry rY ry Ry rY ry Dihybrid Cross RY RY RRYY Ry RRYy rY RrYY ry RrYy Ry rY ry RRYy RrYY RrYy RRyy RrYy Rryy RrYy rrYY rrYy Rryy rrYy rryy Round/Yellow: Round/green: 9 3 wrinkled/Yellow: 3 wrinkled/green: 1 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio 24 Why eye color changes in people is unknown The trait for eye color actually has three alleles: AaBbCc This chart is used to illustrate the variety of eye colors Mendel’s Laws The law of segregation – The two members of a gene pair (alleles) segregate (separate) from each other in the formation of gametes. Half the gametes carry one allele, and the other half carry the other allele. Mendel’s Laws The law of independent assortment – Genes for different traits assort independently of one another in the formation of gametes Other Monohybrid Crosses Incomplete dominance – a form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely dominant over the other allele This results in a combined phenotype. Other Monohybrid Crosses Codominance – Two alleles are expressed (multiple alleles) in heterozygous individuals Two alleles that are both dominant Example: blood types Key A = IA B = IB O=i A and B are dominant over O Other Monohybrid Crosses Genotypes Type A = IAIA or IAi Type B = IBIB or IBi Type AB = IAIB Type O = ii Phenotypes AA or AO BB or BO AB OO Other Monohybrid Crosses Sex-Linked traits – Traits (genes) located on sex chromosomes X – Female sex chromosome Y – Male sex chromosome Many sex-linked traits carried on X chromosomes Pedigree Pedigree – A diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to represent people and lines to represent genetic relationships