* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11.1. Introducing Gregor Mendel
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome-wide association study wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
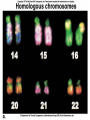
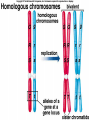
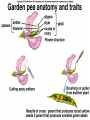
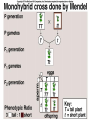
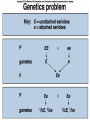
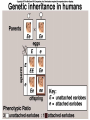
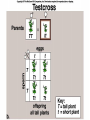
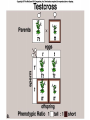
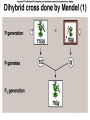
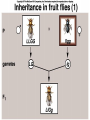
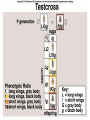
Chapter 14 Biology History Mendel Blending Concept of Inheritance • This theory stated that if parents were different, offspring would possess traits intermediate between those of parents. • Found to be incorrect by Mendel!! History Watson Crick Bacterial Genetic Engineering and BioWarfare Bacterial Genetic Mutation Mendel's law of segregation: • Organism contains two factors for each trait; • Factors segregate in formation of gametes; • Each gamete contains one factor for each trait. C. Modern Genetics • Homozygous genotypes possess two identical alleles for a trait (PP). • Heterozygous genotypes possess different allele for a particular trait (Pp). C. Modern Genetics • a. Dominant allele masks or hides expression of a recessive allele • b. Recessive allele is an allele that exerts its effect only in the homozygous state C. Modern Genetics • a. Genotype refers to the alleles an individual receives at fertilization. • b. Phenotype refers to the physical appearance of the individual. A. monohybrid crosses • A hybrid is the product of parent organisms that are true-breeding for distinctly different forms of a single trait. A. monohybrid crosses P generation = parents F1 generation = first-generation F2 generation = second-generation Multiplicative law of probability • Chance of inheriting a specific allele from one parent and a specific allele from another is 1/2 x 1/2 or 1/4 Figuring the Probable Results EE = 1/2 × 1/2 = ¼ eE = 1/2 × 1/2 = ¼ Ee = 1/2 × 1/2 = ¼ ee = 1/2 × 1/2 = 1/4 Additive law of probability is sum of individual probabilities of each way an event can occur; 1/4 + 1/4 + 1/4 = 3/4. F. Punnett Square Figures for You • In a Punnett square, all possible types of alleles are lined up vertically and horizontally • every possible combination is placed in squares. A. Dihybrid Crosses. • 1. A dihybrid cross is an experimental cross between two parent organisms that are true-breeding for different forms of two traits. The End.