* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells - Fall River Public Schools
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
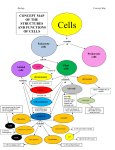
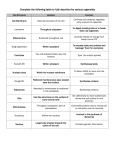
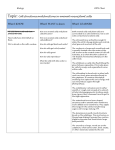
CELLS Prokaryotic cells Simple & Small Bacteria cells Eukaryotic cells Bigger & Complex All cells EXCEPT Bacteria cells -A cell is the SMALLEST unit of LIFE -Characteristics of LIFE: (all living things can do or have these) 1. Movement- ALL living things move 2. Growth- ALL living things grow 3. Death- ALL living things die 4. Reproduction- ALL living things have the ability to reproduce 5. Gas exchange- ALL living things take in a gas & release another gas 6. Heredity- ALL living things have genetic information (DNA and/or RNA) 7. Metabolism- ALL living things need energy 8. Sensitivity- ALL living things respond to their environment 9. Homeostasis- ALL living things maintain and internal/external balance 10. Complexity- ALL living things are made of 1 or more cells There are 2 types of cells: 1. Prokaryotes: (Prokaryotic cells) • These cells are extremely SMALL in size • These cells are very SIMPLE • Types of organism: ALL BACTERIA 2. Eukaryotes: (Eukaryotic cells) • These cells are BIGGER in size • These cells are more COMPLEX • Types of organism: EVERYTHING EXCEPT BACTERIA CELL THEORY: 1. All LIVING things are made up of CELLS 2. All cells come from other CELLS 3. The cell is the basic unit of LIFE. EUKARYOTIC ORGANELLE NOTES: Organelle- tiny structures found inside CELLS - each organelle has it’s own SHAPE & JOB -What are some organelles that you’ve learned about in the past? -CELL MEMBRANE, NUCLEUS, MITOCHONDRIA, ER, RIBOSOME, GOLGI BODY, LYSOSOME, VACUOLE, CELL WALL, CENTRIOLES, & CHLOROPLAST CELL MEMBRANE: (plasma membrane) JOB- let’s molecules IN & OUT of the cell NICKNAME- “BOUNCER” LOCATION- OUTSIDE the cell TYPES OF CELLS- PLANT & ANIMAL cells -The cell membrane is made of 2 organic molecules: PROTEIN & LIPIDS Vocabulary Words: Phospholipid- MADE OF 1 GLYCEROL & 2 FATTY ACIDS Hydrophobic- AFRAID OF WATER (FATTY ACIDS) Hydrophilic- LOVES WATER (GLYCEROL) NUCLEUS: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/insideacell JOB- tells the CELL what to DO NICKNAME- “BRAIN” LOCATION- INSIDE the cell in the CYTOPLASM (gel) TYPES OF CELLS- PLANT & ANIMAL cells -The membrane of the nucleus is called the NUCLEAR ENVELOPE -The ‘dark spot’ is the NUCLEOLUS -2 forms of DNA: -1. CHROMATIN: -’loose’ DNA (in this form MOST of the time) -2. CHROMOSOME: - ‘tight’ DNA (only in this form when the cell is going to divide) / MITOCHONDRION (singular): MITOCHONDRIA (plural) JOB- breaks down FOOD to make ENERGY (this process is called: Cellular Respiration) NICKNAME- “POWERHOUSE” LOCATION- INSIDE the cell in the CYTOPLASM (gel) TYPES OF CELLS- PLANT & ANIMAL cells -The ‘folds’ of the inner membrane are called CRISTAE -All these folds allow the mitochondria to make LOTS OF ENERGY very QUICKLY (by increasing surface area) - The liquid inside the mitochondrion is the MATRIX http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/insideacell/ ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER): 1. ROUGH ER – (rER) JOB- transports PROTEINS throughout the cell NICKNAME- “HIGHWAY” LOCATION- INSIDE the cell in the CYTOPLASM (gel) TYPES OF CELLS- PLANT & ANIMAL cells -The ‘dots’ on the rough ER are called RIBOSOMES -These ‘dots’ make PROTEIN http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/insideacell/ 2. SMOOTH ER – (sER) job- for STORAGE found- INSIDE the cell in the CYTOPLASM (gel) type of cells- PLANT & ANIMAL cells RIBOSOMES: JOB- makes PROTEIN NICKNAME- “PROTEIN SHAKE” LOCATION- 2 places- 1. INSIDE the cell in the CYTOPLASM (gel) 2. attached to the ROUGH ER TYPES OF CELLS- PLANT & ANIMAL cells GOLGI APPARATUS (aka- GOLGI COMPLEX, GOLGI BODY ) JOB- SORTS, PACKAGES & PROCESSES proteins NICKNAME- “WAREHOUSE” LOCATION- INSIDE the cell in the CYTOPLASM (gel) TYPES OF CELLS- PLANT & ANIMAL cells http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/insideacell/ LYSOSOME: JOB- digests old ORGANELLES & waste NICKNAME- “POISON PILL” LOCATION- INSIDE the cell in the CYTOPLASM (gel) TYPES OF CELLS- ANIMAL cells ONLY!! -Inside the lysosome are ENZYMES that help break things down -If the lysosome were to BURSTthe cell would DIE http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/insideacell/ VACUOLE: JOB- stores stuff like WATER NICKNAME- “BACKPACK” LOCATION- INSIDE the cell in the CYTOPLASM (gel) TYPES OF CELLS- PLANT & ANIMAL cells SIZE- Vacuoles are LARGE in plant cells -Vacuoles are SMALL in animal cells PLANT CELL: ANIMAL CELL: CELL WALL: JOB- gives plant cells its SQUARE SHAPE NICKNAME- “GATEKEEPER” LOCATION- OUTSIDE the cell membrane TYPES OF CELLS- PLANT cells ONLY!! **Do you remember what type of carbohydrate is found in the cell wall?** CELLULOSE CENTRIOLES: JOB- helps the cell DIVIDE NICKNAME- “SCISSORS” LOCATION- INSIDE the cell in the CYTOPLASM (gel) TYPES OF CELLS- ANIMAL cells ONLY!! CHLOROPLAST: JOB- takes in SUNLIGHT to make FOOD (This process is called: PHOTOSYNTHESIS) NICKNAME- “CHEF” LOCATION- INSIDE cell in the CYTOPLASM (gel) TYPES OF CELLS- PLANT cells ONLY!! -The green color of plants is due to the chemical called CHLOROPHYLL -Inside the chloroplast are membranes called THYLAKOID MEMBRANES -Stacks of thylakoid membranes are called GRANA -The liquid inside the chloroplast is the STROMA http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/insideacell/ COMPARE & CONTRAST: PROKARYOTIC CELLS SIMILARITIES: DIFFERENCES: EUKARYOTIC CELLS COMPARE & CONTRAST: PLANT CELLS ANIMAL CELLS SIMILARITIES: DIFFERENCES: