* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 30 Nov GPE
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
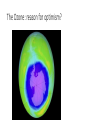
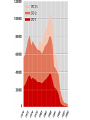
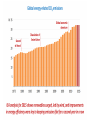
Globalization and the Environment What is today’s most pressing environmental problem? • What should be done about it? • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uULTKOJY9M •Is Globalization bad for the environment? The pro-globalization case Poverty as a cause of environmental problems • Deforestation • Desertification • Unsanitary water • Population growth • Downward spiral Environmental Kuznets Curve Environmental Kuznets Curve • Citizens’ demands • Firms’ and governments’ financial and institutional capacity • Industry to services • Eg: Japan Free Trade • Comparative advantage and efficiency • Technology • Competition and productivity • Price signals • Cleaner industries • Market access. Eg: California emissions standards • Green markets MNCs • Technologies, expertise and funds. Eg: SSA and NK. • Higher standards: tech and management; pressure; codes of conduct and risk management; efficiency and competitiveness. • Voluntary trend to wards ‘greening’. • ‘Tunnel through’ K curve. Critics • Stuck along K curve • Irreplaceable losses • Cumulative change and crisis • Not all pollutants. Eg: CO2. • Relocated polluters. Eg: Japan. • Unequal consumption. • Consumerism. • Production and consumption distance. • Unsustainable growth and consumption. • Prices of traded goods don’t reflect costs. • Race to the bottom: pollution havens and double standards. • North exploiting South: pollution and unsustainable resource exports. • Illegal and destructive practices. Eg: loggers, miners, oil comps, chemical comps. Why is it difficult to tackle environmental challenges like climate change? • http://www.theonion.com/article/marxists-apartment-a-microcosmof-why-marxism-does-1382 4 main types of goods • “Private goods” are excludable: it is possible to prevent others from getting them. There is also rivalry for private goods. If you have one, it means that no one else can have it. • “Public goods” are nonexcludable and nonrivalrous • “Club goods” are excludable and nonrivalrous. • “Common goods” are nonexcludable and rivalrous. • public goods: underprovision; free riders • common goods: the “tragedy of the commons” – Garrett Hardin • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bs2P0wRod8U • Elinor Ostrom: • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qr5Q3VvpI7w Externalities • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1Jlyv1hCTr0 The Ozone: reason for optimism? Ozone depletion • Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) • 1985: ‘hole’ found over Antarctica • 1987 Montreal Protocol: ltd CFC and halon production • 1990: South agreed to phase out. • MP parties created Multilateral Fund for the Implementation of MP • More conferences • http://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-36674996 Reasons • Mid-1980s: 21 firms in 16 countries; 88% in North • #1 producer DuPont sought substitutes and phased out CFCs • Different for climate change? • https://www3.epa.gov/climatechange/test/climatechange/ghgemissi ons/global.html • https://www.theguardian.com/news/datablog/2011/jan/31/worldcarbon-dioxide-emissions-country-data-co2 12 December 2015 Paris Climate Change Agreement • 195 countries • To keep global temperatures "well below" 2.0C (3.6F) above preindustrial times and "endeavour to limit" them even more, to 1.5C • To limit the amount of greenhouse gases emitted by human activity to the same levels that trees, soil and oceans can absorb naturally, beginning at some point between 2050 and 2100 • To review each country's contribution to cutting emissions every five years so they scale up to the challenge • For rich countries to help poorer nations by providing "climate finance" to adapt to climate change and switch to renewable energy. • Christiana Figueres: • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MIA_1xQc7x8 http://www.nytimes.com/2016/11/22/us/poli tics/donald-trump-visit.html • On climate change, Mr. Trump refused to repeat his promise to abandon the international climate accord reached last year in Paris, saying, “I’m looking at it very closely.” Despite the recent appointment to his transition team of a fierce critic of the Paris accords, Mr. Trump said that “I have an open mind to it” and that clean air and “crystal clear water” were vitally important. http://www.nytimes.com/2016/11/29/business/e nergy-environment/china-coal-climatechange.html?_r=0 • America’s uncertain stance toward global warming under the coming administration of Donald J. Trump has given China a leading role in the fight against climate change. It has called on the United States to recognize established science and to work with other countries to reduce dependence on dirty fuels like coal and oil. But there is a problem: Even as it does so, China is scrambling to mine and burn more coal. A lack of stockpiles and worries about electricity blackouts are spurring Chinese officials to reverse curbs that once helped reduce coal production. Mines are reopening. Miners are being lured back with fatter paychecks.