* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download human anatomy - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
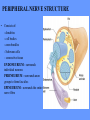
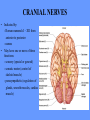
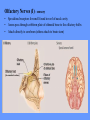
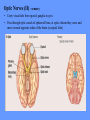
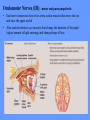
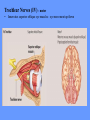
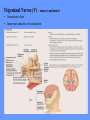
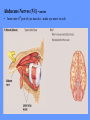
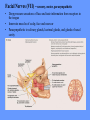
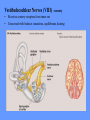
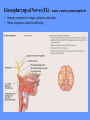
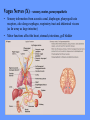
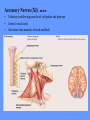
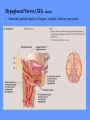
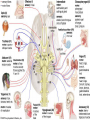
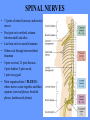
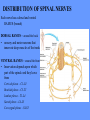
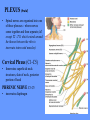
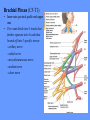
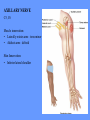
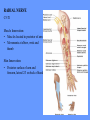
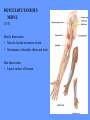
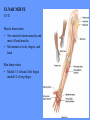
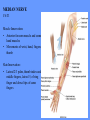
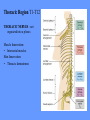
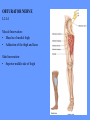
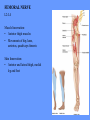
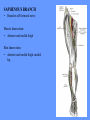
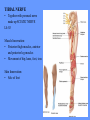
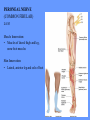
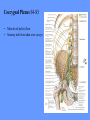
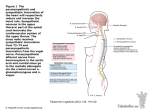
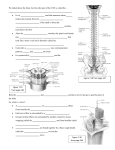
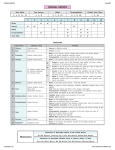
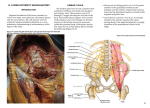
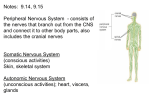
HUMAN ANATOMY LECTURE TWELVE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM • PNS consists of all the neuron cell bodies and process located outside the brain and spinal cord • Collects info from sources inside and on the surface of the body • Relays info by way of afferent fibers to the CNS • Efferent fibers relay info from CNS to muscles and glands • Divided into two parts: - 12 pairs of cranial nerves - 31 pairs of spinal nerves PERIPHERAL NERVE STRUCTURE • Consists of: - dendrites - cell bodies - axon bundles - Schwann cells - connective tissue ENDONEURIUM - surrounds individual neurons PERINEURIUM - surrounds axon groups to form fascicles EPINEURIUM - surrounds the entire nerve fibre CRANIAL NERVES • Indicated by: - Roman numerals I – XII from anterior to posterior - names • May have one or more of three functions: - sensory (special or general) - somatic motor (control of skeletal muscle) - parasympathetic (regulation of glands, smooth muscles, cardiac muscle) Olfactory Nerves (I) - sensory • Specialized receptors for smell found in roof of nasal cavity • Axons pass through cribform plate of ethmoid bone to the olfactory bulbs • Attach directly to cerebrum (others attach to brain stem) Optic Nerves (II) - sensory • Carry visual info from special ganglia in eyes • Pass through optic canals of sphenoid bone, at optic chiasm they cross and move toward opposite sides of the brain (occipital lobe) Oculomotor Nerves (III) - motor and parasympathetic • Each nerve innervates four of six extra-ocular muscles that move the eye and raise the upper eyelid • Also controls intrinsic eye muscles that change the diameter of the pupil (adjust amount of light entering) and change shape of lens Trochlear Nerves (IV) - motor • Innervates superior oblique eye muscles - eye movement up/down Trigeminal Nerves (V) – sensory and motor • Sensation to face • Innervates muscles of mastication Abducens Nerves (VI) - motor • Innervates 6th pair of eye muscles - make eye move to side Facial Nerves (VII) – sensory, motor, parasympathetic • Deep pressure sensations of face and taste information from receptors in the tongue • Innervate muscles of scalp, face and near ear • Parasympathetic to salivary glands, lacrimal glands, and glands of nasal cavity Vestibulocochlear Nerves (VIII) - sensory • Receives sensory receptors from inner ear • Concerned with balance sensations, equilibrium, hearing Glossopharyngeal Nerves (IX) – sensory, motor, parasympathetic • Sensory responses to tongue, pharynx, and palate • Motor responses control swallowing Vagus Nerves (X) – sensory, motor, parasympathetic • Sensory information from acoustic canal, diaphragm, pharyngeal taste receptors, also along esophagus, respiratory tract and abdominal viscera (as far away as large intestine) • Motor functions affect the heart, stomach, intestines, gall bladder Accessory Nerves (XI) - motor • Voluntary swallowing muscles of soft palate and pharynx • Control vocal cords • Also innervates muscles of neck and back Hypoglossal Nerves (XII) - motor • Innervates skeletal muscles of tongue - controls voluntary movements SPINAL NERVES • 31 pairs of mixed (sensory and motor) nerves • First pair exit vertebral column between skull and atlas • Last four exit via sacral foramina • Others exit through intervertebral foramina • 8 pair-cervical, 12 pair-thoracic, 5 pair-lumbar, 5 pair-sacral, 1 pair-coccygeal • Most organized into 3 PLEXUS where nerves come together and then separate (cervical plexus, brachial plexus, lumbosacral plexus) DERMATOMAL MAP • Spinal nerves indicated by capital letter and number • DERMATOMAL MAP - skin area supplied with sensory innervation by spinal nervers DISTRIBUTION OF SPINAL NERVES Each nerve has a dorsal and ventral RAMUS (branch) DORSAL RAMUS – around the back • sensory and motor neurons that innervate deep muscles of the trunk VENTRAL RAMUS – around the front • Innervation depends upon which part of the spinal cord they leave from Cervical plexus – C1-C4 Brachial plexus – C5-T1 Lumbar plexus – T1-L4 Sacral plexus – L4-L5 Cooccygeal plexus – S4-S5 PLEXUS (braid) • Spinal nerves are organized into one of three plexuses - where nerves come together and then separate (all except T2 - T11 which extend around the thorax between the ribs to innervate intercostal muscles) Cervical Plexus (C1-C5) • Innervates superficial neck structures, skin of neck, posterior portion of head PHRENIC NERVE C3-C5 • innervates diaphragm Brachial Plexus (C5-T1) • Innervates pectoral girdle and upper arm • Five rami divide into 3 trunks that further separate into 6 cords that branch off into 5 specific nerves: - axillary nerve - radial nerve - musculocutaneous nerve - median nerve - ulnar nerve AXILLARY NERVE C5, C6 Muscle innervation: • Laterally rotates arm - teres minor • Adducts arm - deltoid Skin Innervation: • Inferior lateral shoulder RADIAL NERVE C5-T1 Muscle Innervation: • Muscles located in posterior of arm • Movements at elbow, wrist and thumb Skin Innervation: • Posterior surface of arm and forearm, lateral 2/3 on back of hand MUSCULOCUTANEOUS NERVE C5-T1 Muscle Innervation: • Muscles located at anterior of arm • Movements at shoulder, elbow and wrist Skin Innervation: • Lateral surface of forearm ULNAR NERVE C8-T1 Muscle Innervation: • Two anterior forearm muscles and most of hand muscles • Movements at wrist, fingers, and hand Skin Innervation: • Medial 1/3 of hand, little finger, medial1/2 of ring finger MEDIAN NERVE C6-T1 Muscle Innervation: • Anterior forearm muscle and some hand muscles • Movements of wrist, hand, fingers, thumb Skin Innervation: • Lateral 2/3 palm, thumb index and middle fingers, lateral ½ of ring finger and dorsal tips of same fingers Thoracic Region T1-T12 THORACIC NERVES - not organized into a plexus • Muscle Innervation: • Intercostal muscles Skin Innervation: • Thoracic dermatomes Lumbosacral Plexus • Originates from nerves of the lumbar plexus (L1-L4) - obturator nerve - femoral nerve - saphenous branch • Also nerves from the sacral plexus (L4-S4) - tibial nerve - peroneal nerve OBTURATOR NERVE L2-L4 Muscle Innervation: • Muscles of medial thigh • Adduction of the thigh and knee Skin Innervation: • Superior middle side of thigh FEMORAL NERVE L2-L4 Muscle Innervation: • Anterior thigh muscles • Movements of hip, knee, sartorius, quadriceps femoris Skin Innervation: • Anterior and lateral thigh, medial leg and foot SAPHENOUS BRANCH • Branches off fermoral nerve Muscle Innervation: • Anterior and medial thigh Skin Innervation: • Anterior and medial thigh, medial leg TIBIAL NERVE • Together with peroneal nerve make up SCIATIC NERVE L4-S3 Muscle Innervation: • Posterior thigh muscles, anterior and posterior leg muscles • Movement of hip, knee, foot, toes Skin Innervation: • Sole of foot PERONEAL NERVE (COMMON FIBULAR) L4-S3 Muscle Innervation: • Muscles of lateral thigh and leg, some foot muscles Skin Innervation: • Lateral, anterior leg and sole of foot Coccygeal Plexus S4-S5 • Muscles of pelvic floor • Sensory info from skin over coccyx PNS DISORDERS General Disorders: Anesthesia - loss of sensation • Hyperesthesia - increased sensitivity to pain, pressure, light • Paesthesia - tingling, prickling, burning • Neuralgia - nerve inflammation causing stabbing pain • Sciatica - pain radiating down back of thigh and leg Infections: • • • • Herpes - skin lesions Shingles (herpes zoster) - adult chickenpox Poliomyelitis - infantile paralysis Anesthetic leprosy - bacterial infection of peripheral nerves Genetic and Autoimmune Disorders: • Myasthenia gravis - results in fatigue and muscular weakness due to inadequate ACh receptors