* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download a)write short notes about the anatomy of optic nerve
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
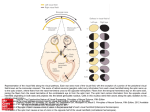
($..l.Al\ y.b ~ - jl.li.: ~~ 2013-2012 WI ~ - ~till ~yJI - ~~l ;j1.4 u~~ ~j~\ 4~"J\ y~ ~l ~y3:U ;j1.4 j u-.F- .)At:i ~ ~. I,..·· Neuroanatomy a)write short notes about the anatomy of optic nerve Optic Nerve (Cranial Nerve II) Origin of the Optic Nerve The fibers ol'the optic nerve are the axons orthe cells in the ganglionic layer of the retina. They converge on the o(1tic disc and exit li'ol11 the eye. about 3 or 4 mm to the nasal side of its center. as the optic nerve The libel's orthe optic nerve arc myelinated. but the sheaths arc j(JI'med li'om oligodendrocytes rather than Schwann cells. sincc the optic nerve is comparable to a tract within the central nervous system, The optic nerve leaves the orbital cavity through the optic canal and unites with the optic nerve ol'the opposite side to larm the optic chiasma Optic Chiasma In the chiasma. the libel'S tj'om the nasal (rnedial) Iwlf of each retina. including thc nasal half 01' the macula. cross the midline and enter the optic tract or the o(1posite side. while the fibers hom the tel11poral (lateral) half or each retina. including the tem poral hal f of the macu lao pass posteriorly in the optic tract of the same side Optic Tract The optic tract emerges I'rom the optic chiasma and passes (1osterolaterally around the cerebral peduncle, Most of the tibers no\\ terminate by synapsing with nerve cells in the lateral geniculate body. which is a small projection from the posterior part of the thalamus, A few of the tibers pass to the prctectal nucleus and the superior colliculus of the midbrain and are concerned with light retlexes Lateral Geniculate Body The lateral geniculate body is a small, oval swelling projecting hom the pulvinar of the thalamus. It consists of six layers of cells, on which synapse the axons of the optic tract. The axons of the nerve cells within the geniculate body leave it to form the optic radiation Optic Radiation 1 The fibers of the optic radiation are the axons of the nerve cells of the lateral geniculate body. The tract passes posteriorly through the retrolenticular part orthe internal capsule and terminates in the visual cortex (area 17) Neurons of the Visual Pathway Four neurons conduct visual impulses to the visual cortex: (1) rods and cones, which are specialized receptor neurons in the retina; (2) bipolar neurons, which connect the rods and cones to the gangl ion cells: (3) ganglion cells, whose axons pass to the lateral geniculate body: and (4) neurons of the lateral geniculate bodv. whosc axons pass to the cerebral cortex b) describe the middle cranial fossa consists of a small median part and expanded lateral parts The median raised part is formed by the body of the sphenoid. and the expanded lateral parts rorm concavities on either side. which lodge the temporal lobes o]'the cerebral hemispheres It is bounded anteriorlv by the sharp posterior edges orthe lesser wings of the sphenoid p~1'iL<;riorlv by the superior borders 0 r the petrous parts 0 f the tem pora I bones. l:'.!tcraLLY lie the squamous parts of the temporal bones. the greater wings orthe sphenoid. and the parietal bones. The floor oreach lateral part of the middle cranial fossa is larllled by the greater wing ol'the sphenoid alld the squamous and petrous parts of the temporal bone. c) enunlerate the nuclei of one of the followings: - Vestibulocochlear Nuclei Olivary Nuclear Complex Vcstibulocochlear Nuclei Vestibular comples: (1) medial vestibular IlUCleUS (2) inferior vestibular Ilucleus (3) latcral vestibular nucleus (4) superior vestibular nucleus Cochlear nuclei: (1) anterior cochlear nucleus (2) posterior cochlear nucleus Olivary Nuclear Complex - The largest nucleus of this complex is the inferior olivary nucleus - Smaller dorsal and medial accessory olivary nuclei also are present ?'" ~ \ '-' ....; 11.J \.i;l0..c.:i J~y-' . .' 2 C""