* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WRI116-Research_Review
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Purinergic signalling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor type 1 wikipedia , lookup
VLDL receptor wikipedia , lookup
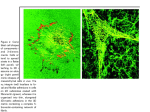
Hidalgo1 Amanda Hidalgo Writing 116 19 November 2013 Translating Integrin Receptors For Detection of Cancer Introduction: Integrins are a group of heterodimer cell surface receptors that are considered as the central extracellular matrix receptors. They convey cell-matrix and cell-to-cell interactions that involve adhesion, invasion, proliferation, and migration. In particular, alpha-v-beta-6 (avb6) and alpha-v-beta-3(avb3) integrins are targets for cancer therapy. Their expression increases the cellular components by the start of carcinoma types to invade tumor cells. Clinical studies tested antibodies and peptides that bind to the integrin receptors such as the fibronectin III domain, AgRP peptide, and cystine knots, as a method to detect cancer; Specifically, the identification of pancreatic cancer by translation of the cysteine knots binding to integrin receptors like, avb6 and avb3. Unfortunately, there are some cases in which avb3 is expressed more in binding with specific antibodies and peptides rather than avb6 integrin. This is because avb3 integrin binds to a vast range of integrin ligands and sequences to regulate cell growth and survival. This review will also include the effectiveness of yeast surface display, fine epitope mapping, and down regulation of the integrin receptor, so in future purposes it will be relevant for potential therapeutic approaches. The Effectiveness of Peptides and Antibodies to Bind with Alpha-v-Beta-3 Integrin The avb6 and avb3 integrin receptors are targets for cancer and applicable for advantages in therapies. In one of the studies, researchers conducted phage cloning in order to bind to the avb3 and avb6 receptors. By using the phage cloning, phage FNfn10 showed Hidalgo2 similarities to the avb3 integrin receptor rather than the avb6 integrin receptor. Kogelberg et al investigated how the single-chain fv-antibody binds to avb3 integrin from the specific loop of a foot-and-mouth-disease virus. From the collected data, a series of antiavb3 scFvs was generated by the insertion of a 17-mer peptide of VPI, composing the prevention of a 20-mer peptide into the CDR-H3. (2) As a result from Kogelberg et al study, the FNfn10-3JCLI4 is a possible effecting agent because of “its ability to recognize avb3 on tumor vasculature”. The figure on the left represents the prevention of glass capillary tube formations of FNfn10-3JCL14. By the in vitro inhibition, there are still investigations in which to explore the improvements of phage vector FNfn10-3JCL14 as binding agent with the avb3 integrin. Not only did Kogelberg et al study the significance of avb6, but Ylipalosaari et al studied how the avb6 integrin down-regulates a matric metalloproteinases expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells (OSCC). The matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are able to divide into various subdivisions and have enzymatic activity. This is useful in the expression in OSCCs because the upregulation of avb6 promotes OSCC invasion in vitro and in vivo which indicates the transfected OSCC cells to form a proteolytic cascade resulting in activation of the uPA to MMP-3 to MMP-9 pathway (6). Ylipalosaari et al studied concluded in the research that the “inhibition of avb6 induces MMP-13 protein expression by Western blotting, gelatin zymography, and reverse zymography”. The research allowed the treatment with anti- Hidalgo3 avb6 antibody to be in C1 and VB6 cell lines. With the TIMP-1 levels being distinguishable in C1 and VB6 cells the avb6 antibody up-regulated MMP-9 expression in order to invade OSCCs. Yeast Surface Display Most of the studies use a yeast surface display to examine the high specificity and affinity of the integrin receptors. The yeast surface display is generated for the cystine-knot library in order for avb3 integrin receptor to be tested for the ability for bind to express human cancer cells. The figure below explains how Silverman et al conducted binding titrations. The data represents the arbitrary mean of fluoresce units for 10^4 cells bound with varying concentrations of the AgRP peptides and stained with fluorescein-labeled anti-6x-His antibody. (5) Thus, the results showed that the AgRP peptide is able to bind the integrin receptor with high affinity and can be potential in tumor imaging in animal models to further out targeting of integrins on cancer cells. This will create cystine-knot scaffold to be of greater importance clinically and scientifically. The yeast surface display is effective for “finer, residue-level resolution of antibodyantigen binding interactions”(1). In spite of Silverman et al research using yeast surface display, Lipovsek et al used a different approach on using the yeast surface display. Lipovsek et al investigated Fn3 variants with sub-nanomolar affinity can be selected from Hidalgo4 libraries with only one or two randomized loops (3). Fn3 variants will bind with protein and integrin receptors in order to recognize distinct structures of cancer cell targets. When using the yeast surface display, the Fn3 variants that were chosen bond with a hen egg white lysozyme. The hen egg white lysozyme is used as an antigen extensively in structural studies of antibody-antigen binding (3). With the first set of selected antibody mimics that bonded with the hen egg white lysozyme, yeast populations displayed libraries BC7, FG7, 2L14, and BF14 to show the “affinity-maturation” from libraries BFs 1,2, and 3. Out of the libraries, FG7 constructed the random residues in loop FG of human FN3 to be closely related as a selected clone. The construction of the residues in loop FG of human FN3 makes the option of binding properties to be instantaneous and accurate for the purification of individual clones. Researchers are expected to confirm the structural studies of variants, such as FN3, with cystine pairs in complex with lysozymes to contribute in binding surfaces on antibody-mimic molecules. Lipovsek et al explained in the study how in vitro of the FN-3 based antibody could have “the tendency of the system to re-evolve the disulfide after the cystine positions are randomized during affinity maturation” (3). Thus, integrin receptors will improve on higher affinity maturation and specificity. Enhancement AVB3 By Engineering Fibronectin Type III Domain Richards et al investigated that “high- affinity and high-specificity variants of FNfn10 to a particular integrin could be engineered by optimizing residues surrounding the integrinbinding RGD sequence in the flexible FG loop”(4). They determined that the fibronectin is able to bind with the avb3 integrin in vivo by means of the RGD sequence. The modified FNfn10 with higher specificity and affinity for avb3 can result in residues of Hidalgo5 amino acids surrounding the RGD sequence in a FG loop. By doing this, avb3 is capable of binding to a great range of RGD ligands, which are useful in staining human umbilical vein endothelial cells in cytometric assay. Results of the study showed FNfn10-3JCLI4 were able to bind to avb3 in half-log increments from .0001ng/ml to 0.1ng/ml, corresponding to molar concentrations of 8pM to 8nM(4). “The biotinylated FNfn103JCLI4 or FNfn10-WT wee added to wells coated with 5ng/ml concentrations of different purified integrins”(4). This is significant by which the plate-bound FNfn103JCLI4 was detected for those that have been coated with avb3, thus creating a high affinity. The avb3 binding with the FNfn10 clones that were discovered in the RGD sequence has similarities with the purified monomeric FNfn10-protiein by the stability and cell adhesion effect in vitro of formation of the capillary tubes. As an outcome of Richard et al study, using bio-panning screening can purify FNfn10-3JCLI4 protein to bind to immobilized human avb3 integrin with much higher affinity that FNfn10-WT and exhibit only background binding to other purified integrins (4). Conclusion Conducting more research on avb3 and avb6 integrin receptors will help improve therapeutic procedures such as cancer. Avb3 integrin a cell surface receptor tht multifunction’s in normal cell growth that may contribute to oncogenesis. Through the effectiveness of peptides and antibodies, using yeast surface display methods, and engineering proteins to associate the binding of either avb3 and avb6 integrins, researchers can explore various approaches in cancer cells and tumor vasculature. They are able to pinpoint the target cells and modify antibodies or sequences of RNA/DNA to inhibit the high affinity and specificity of the integrin maturation. These methods could Hidalgo6 potentially help patients with cancer and possibly prevent individuals in promoting cancer by the significance of human integrin receptors eliminating the danger cancer cells. References 1. Chao G, Cochran JR, Dane Wittrup K. 2004. Fine epitope mapping of antiepidermal growth factor receptor antibodies through random mutagenesis and yeast surface display. J Mol Biol 342(2): 539-50. 2. Kogelberg H, Tolner B, Thomas GJ, Di Cara D, Minogue S, Ramesh B, Sodha S, Marsh D, Lowdell MW, Meyer T, et al. 2008. Engineering a single-chain fv antibody to αvβ6 integrin using the specificity-determining loop of a foot-andmouth disease virus. J Mol Biol 382(2): 385-401. 3. Lipovšek D, Lippow SM, Hackel BJ, Gregson MW, Cheng P, Kapila A, Wittrup KD. 2007. Evolution of an interloop disulfide bond in high-affinity antibody mimics based on fibronectin type III domain and selected by yeast surface display: Molecular convergence with single-domain camelid and shark antibodies. J Mol Biol 368(4): 1024-41. 4. Richards J, Miller M, Abend J, Koide A, Koide S, Dewhurst S. 2003. Engineered fibronectin type III domain with a RGDWXE sequence binds with enhanced affinity and specificity to human αvβ3 integrin. J Mol Biol 326(5): 1475-88. 5. Silverman AP, Levin AM, Lahti JL, Cochran JR. 2009. Engineered cystine-knot peptides that bind αvβ3 integrin with antibody-like affinities. J Mol Biol 385(4): 1064-75. 6. Ylipalosaari M, Thomas GJ, Nystrom M, Salhimi S, Marshall JF, Huotari V, Tervahartiala T, Sorsa T, Salo T. 2005. αvβ6 integrin down-regulates the MMP13 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res 309(2): 27383.