* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Transport Notes
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
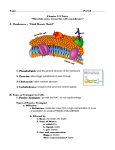
Visit www.worldofteaching.com For 100’s of free powerpoints Protect cell 2. Flexible 3. Maintains Homeostasis 4. Selectively permeable - allows some molecules in, others are kept out 1. 1. Phospholipid Bilayer – 2 layers of lipids with a phosphate group attached to them. 2. Cholesterol – Stabilizes the phospholipids and prevents the fatty acid chains from sticking together. 3. Transport Proteins – Allow certain materials to pass through the membrane How Does It Look? Fluid Mosaic Model – Expression used to describe the flexible membrane of a cell. Phospholipids of the membrane shift and move like a fluid. Backbone Phospholipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Q: What are three components of a cell membrane? A: phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol, transport proteins Q: What are the three components of a phospholipid? A: Hydrophilic (phosphate) head, Glycerol Backbone, Hydrophobic (fatty acid) tail 1. Passive Transport – No Energy Required a. Diffusion – movement of particles; affected by temperature, pressure, & concentration 2. b. Facilitated Diffusion – use of proteins c. Osmosis – movement of water Active Transport – Energy (ATP) Required a. Sodium-Potassium Pump – use of ions b. Endocytosis – take in c. Exocytosis – take out (exit) Q: What are three types of passive transport? A: Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion, Osmosis Q: Which type of transport requires ATP? A: Active Q: What 3 factors affect diffusion? A: Concentration, Temperature, Pressure Methods of Transport Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Movement from one side of a membrane to another, unfacilitated Movement of water from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Movement from one side of a membrane to another, unfacilitated AEROSOL SPRAY FOOD COLORING Diffusion Explanation Osmosis Explanation A cell placed in this soln. will swell Water leaves the tube A cell placed in this soln. will shrink Water enters the tube Solutions are made of two things: a solute and a solvent What is a Solvent? What is a Solute? Solvent - the liquid into which the solute is poured and dissolved. Water is the universal solvent. Solute - substance that is dissolved or put into the solvent. Salt and sucrose are solutes. (Osmotic Solutions & Aqueous Solutions both Involve to Water) 1. ISOTONIC SOLUTION Both solutions (inside & outside of cell) have same concentrations of solute. (Equal Concentrations) Osmosis does not occur No net movement of water Cell remains the same “Iso- “Keep it So” See next slide for type #2 2. HYPOTONIC SOLUTION Solute (salt) outside cell is lower than solvent (water) (More water outside than inside) Osmosis occurs Water moves into the cell Cell swells “Hypo-Big O” See next slide for type #3 3. HYPERTONIC SOLUTION Solute (salt) outside cell is higher than solvent (water) (More water inside than outside) Osmosis occurs Water moves out of the cell Cell shrinks “Hyper-Smaller” WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF OSMOTIC SOLUTIONS? OSMOTIC (AQUEOUS) SOLNS ISOTONIC SOLUTION HYPOTONIC SOLUTION CAUSE Both solutions (inside & outside of cell) have same concentrations of solute. (Equal) Solute (salt) outside cell is lower than solvent (water) (More water outside than inside) EFFECT Osmosis does not occur No net movement of water Cell remains the same “Iso- Stay So” or “Keep it So” Osmosis occurs Water moves into the cell Cell swells “Hypo-Big O” HYPERTONIC SOLUTION Solute (salt) outside cell is higher than solvent (water) (More water inside than outside) Osmosis occurs Water moves out of the cell Cell shrinks “Hyper-Smaller” Plant and Animal Cells put into various solutions Q: When you are in the den & are able to smell food in the kitchen, what process is allowing you to smell the aroma? A: Diffusion Q: Is sugar a solute or solvent? A: Solute Q: What are 3 types of osmotic solutions? A: Isotonic, Hypotonic, Hypertonic Q: If a cell is placed in a strong salt solution, explain what will happen to the cell? A: It will shrink due to the lack of water outside the cell. When a person is given an I.V., the fluid has a little salt in it just like our blood. Explain how the use of distilled water in place of saline solution would up set homeostasis. Homeostasis would be upset because there would be more salt inside a cell then outside a cell. The water would move into the cell causing it to burst. Why does eating popcorn make you thirsty? Popcorn is very salty and may cause water to leave the cells of your mouth and through due to diffusion. This makes a person thirsty. NORMAL CELLS DEHYDRATED CELLS OSMOSIS DEMONSTRATION IODINE & CORNSTARCH CELLULAR TRANSPORT DEMO https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DFhlqgMy1Dk SOLUTON A SOLUTION B SOLUTION C ________ cell 2. ___________ 3. Maintains __________ 4. _____________ _________- allows some molecules in, others are kept out 1. 1. ______________ Bilayer – 2 layers of lipids with a phosphate group attached to them. 2. ______________ – Stabilizes the phospholipids and prevents the fatty acid chains from sticking together. 3. Transport ____________ – Allow certain materials to pass through the membrane How Does It Look? _________ __________ Model – Expression used to describe the flexible membrane of a cell. Phospholipids of the membrane shift and move like a fluid. Backbone 1. _________ Transport – No Energy Required a. ____________ – movement of particles; affected by temperature, pressure, & concentration 2. b. Facilitated Diffusion – use of __________ c. __________ – movement of water _________ Transport – Energy (ATP) Required a. Sodium-Potassium Pump – use of ions b_____________– take in c. Exocytosis – take _______ (exit) _______________ of _______________ from an area of _________ concentration to an area of _______ concentration. Movement from one side of a membrane to another, unfacilitated _____________ of ______________from an area of _________ concentration to an area of _______ concentration. Movement from one side of a membrane to another, unfacilitated Solutions are a __________ (homogeneous) _________ that may contain solids, liquids, or gases and are _______ up ______ two parts (_________ & _________) What is a Solvent? What is a Solute? Solvent (what does the dissolving) - the ________ which _________ the solute (substance). __________ is the universal solvent. Solute (what gets dissolved) - _________ that is ___________ or put into the solvent . Salt and sucrose are solutes. (Osmotic Solutions & Aqueous Solutions both Involve Water) 1. ISOTONIC SOLUTION Both solutions (inside & outside of cell) have same concentrations of solute. (Equal Concentrations) Osmosis ______ ______ occur ________ net movement of water Cell remains the ________ “Iso- “Keep it So” See next slide for type #2 2. HYPOTONIC SOLUTION Solute (salt) outside cell is lower than solvent (water) (More water outside than inside) Osmosis ________ _________ moves _______ the cell Cell __________ “Hypo-Big O” See next slide for type #3 3. HYPERTONIC SOLUTION Solute (salt) outside cell is higher than solvent (water) (More water inside than outside) Osmosis _________ __________ moves ______ _____ the cell Cell ___________ “Hyper-Smaller” WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF OSMOTIC SOLUTIONS? OSMOTIC (AQUEOUS) SOLUTIONS CAUSE Both solutions (inside & outside of cell) have same concentrations of solute. (Equal) Solute (salt) outside cell is lower than solvent (water) (More water outside than inside) EFFECT Osmosis does not occur No net movement of water Cell remains the same “Iso- Stay So” or “Keep it So” Osmosis occurs Water moves into the cell Cell swells “Hypo-Big O” Solute (salt) outside cell is higher than solvent (water) (More water inside than outside) Osmosis occurs Water moves out of the cell Cell shrinks “Hyper-Smaller”