* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topics To Know For Chapters 8-10
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
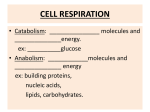
Topics To Know For Chapters 8-10 1. What is the meaning of metabolism. What is associated with a metabolic pathway. - substrate or reactant - catabolism - products - anabolism - enzymes - bioenergetics 2. Know what is meant by energy. Name the two forms of energy and give examples. 3. What is the ultimate energy source for all living things. 4. Know how the first law of thermodynamics is defined. 5. Know how the second law of thermodynamics is defined. - useable energy - entropy - unuseable energy 6. Be able to describe exergonic and endergonic reactions. - reactants - potential energy - products - energy of activation (Eact) - spontaneous reaction 7. Know the characteristics of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). How is it broken down and how is it synthesized? - phosphate groups - phosphorylation - high energy bonds 8. Know what is energy coupling and how does it relate to ATP. 9. Be able to discuss the characteristics of enzymes given in class. - proteins - lock and key model - reversible inhibition - catalyst - induced fit model a. competitive - Eact - optimal conditions b. noncompetitive - ase ending - temperature sensitive - irreversible inhibition - specific - pH sensitive a. nerve gas - active site - inorganic cofactors b. pesticides - enzyme substrate - organic cofactors c. cyanide complex d. penicillin 10. Know what is meant by allosteric regulation. - active form - activator - inactive form - inhibitor 11. Know what is meant by cooperativity. Is it a type of allosteric regulation? 12. Describe how feedback inhibition works. 13. Know what is photosynthesis and how does it relate to autotrophs and heterotrophs. 14. Know the parts of the chloroplast that are related to photosynthesis. How do they function in photosynthesis? - grana (granum) - thylakoid - stroma - thylakiod space 15. Know that photosynthesis involves redox reactions. 16. Know that photosynthesis is divided in two parts. Where in the chloroplast do they take place? - light dependent reactions - chemiosmosis - light independent reactions - phosphorylation - Calvin cycle - oxygen - NADP & NADPH - carbon fixation - photolysis - CO2 reduction - ATP & ADP + phosphate group 17. What is meant by the electromagnetic spectrum? 18. Know that the visible light spectrum is divided into wavelengths or colors. What are photons? 19. Know that chl a is a primary pigment and other pigments are called accessory pigments. - chl a - carotenoid - chl b 20. Which part of the chlorophyll molecule is stimulated by light? - ground state - fluorescence - excited state - magnesium 21. Know what is meant by a photosystem. How many are there? - chlorophyll - reaction center - antenna - P700 - redox - P680 22.Know what happens in noncyclic electron flow. Which part of photosynthesis (two parts) does noncyclic electron flow come under - photolysis - redox - photon - phosphorylation - P680 - chemiosmosis - P700 - NADP and NADPH - O2 - electron flow 23. Know what happens in cyclic electron flow. - photosystem I - no CO2 - phosphorylation - too much NADPH - chemiosmosis 24. Know the events of chemiosmosis discussed in class and where does it take place. - thylakoid membrane - ATP synthase - thylakoid space - electron flow - pH 4 - photosystems I & II - H+ concentration 25. Know what makes the Calvin cycle work or operate. Describe the events taking place in the Calvin cycle. - stroma - PGAL - CO2 - glucose - carbon fixation - NADPH & NADP - CO2 reduction - ATP & ADP + phosphate group - ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) 26. Name two catabolic pathways. - aerobic respiration - NAD - fermentation - FAD - redox reactions 27. Know the three main stages of aerobic cell respiration and where do they take place? - mitochondria - FAD & FADH - glycolysis - substrate phosphorylation - pyruvate to acetyl CoA - oxidative phosphorylation - citric acid cycle Krebs) - CO2 and H2O - ETS - 40 ATP total - chemiosmosis - 38 ATP net - NAD & NADH 28. Know the steps of glycolysis covered in class and where does it take place. - glucose - NAD - PGAL - pyruvic acid - Eact (2 ATP) - anaerobic activity - substrate phosphorylation (4 ATP) 29. Know the steps used to convert pyruvic acid to acetyl CoA. - NAD - CO2 30. Know the steps of the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) covered in class. Know that it takes place twice for each glucose molecule. Where does it take place? - acetyl CoA - NAD & FAD - oxaloacetate - substrate phosphorylation (2 ATP) - citrate - CO2 - alpha ketoglutarate - anaerobic activity 31. Describe the electron transport system covered in class. How does it work ? Where does it take place? - NAD & FAD - O2 - H (atoms) - final hydrogen acceptor - H+ (ions) - aerobic activity - electrons - oxidative phosphorylation 32. Describe the events of chemiosmosis and where does it take place. - mitochondria - H+ (ions) - cristae - H (atoms) - ATP synthase - O2 - ATP - H2O - electrons 33. Account for the ATP produced in aerobic respiration, alcohol fermentation, and lactic acid fermentation. - total ATP - substrate ATP - net ATP - oxidative ATP 34. Compare the efficiency of aerobic respiration and fermentation. 35. Be able to describe the events of alcoholic fermentation. What kind of cells carry out alcoholic fermentation? Which industries depend on this process? - glucose - CO2 - pyruvate - ATP (total and net) - alcohol - substrate phosphorylation 36. Be able to describe the events of lactic acid fermentation. What kind of cells carry out lactic acid fermentation? - skeletal muscle - oxygen debt - glucose - fatigue - pyruvate - facultative anaerobe - lactic acid - ATP (total and net) - strenuous activity - substrate phosphorylation 37. Know that fats and proteins are used to make ATP. How do they enter the metabolic pathway used to breakdown carbohydrates ( glucose )? If you had 50 grams of protein, 50 grams of carbohydrate, and 50 grams of fat, how much energy would we expect to be given off by each type of organic molecule?