* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Physiology Quiz Questions: 1) Purines degrade into what
Survey
Document related concepts
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Human digestive system wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
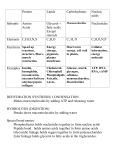
Human Physiology Quiz Questions: 1) Purines degrade into what molecule? 2) What molecule is deposited into the joints when you suffer from gout? 3) What two brush border enzymes aid in the digestion and absorption of nucleic acids? 4) What is ‘de novo synthesis’ of nucleic acids and where does it take place? 5) What is the difference between a nucleoside and a nucleotide? 6) What is the ‘salvage pathway’ for nucleic acids? 7) What is the primary enzyme that catalyzes glycogenesis? 8) What two membrane transporters absorb monosaccharides into the absorptive cell? 9) What is ‘gluconeogenesis’? 10) What causes salivary amylase inactivation? 11) What two monosaccharides is sucrose made up of and what enzyme digests sucrose? 12) What two monosaccharides is maltose made up of and what enzyme digests maltose? 13) What two monsaccharides is lactose made up of and what enzyme digests lactose? 14) What does Glut2 do and where exactly is it located? 15) What is ‘glycogenolysis’? 16) In lipogenesis, what substrate does fatty acid synthetase act on to produce fatty acids? 17) What is transamination? 18) Explain the difference between ketogenic and glucogenic amino acids. 19) What is deamination and what are the products of this process? 20) Who can absorb intact proteins? 21) What is an ‘enterocyte’ and where are they specifically found? 22) What does a dipeptidase act on specifically? 23) How does an aminopeptidase cut? 24) What is the difference between an essential and a non-essential amino acid? 25) What is the component of bile that is responsible for emulsification of fat in the small intestine? 26) What is the name of the rate limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis? 27) What is the difference between a chylomicron and VLDL? 28) What does cholecystokinin (CCK) do? 29) If a triglyceride consists of three 22-carbon long fatty acid tails, how many ATP can be produced from this? 30) What are ‘short chain’ and ‘long chain’ fats (fatty acids)? 31) How are ‘short chain’ and ‘long chain’ fatty acids treated differently by the body? 32) What is HDL used for? 33) What is VLDL used for? 34) What are chylomicrons used for? 35) Does hypoventilation cause respiratory acidosis or respiratory alkalosis? 36) Does hyperventilation cause respiratory acidosis or respiratory alkalosis? 37) If a bulimic loses excess H+ by throwing up, how will the body (blood, lungs, kidneys) compensate to keep blood pH 7.4? (Explain and be sure an mention if the bulimic will hyperventilate or hypoventilate) 38) What cells in the body endocytose both chylomicrons and LDL? 39) Are acetate, acetoacetate and hydroxybutarate ‘keto acids’ or ‘ketones’? 40 Draw a large diagram showing ‘fat’ and ‘cholesterol’ entering your GI tract. What happens to both? How are they absorbed and transported? And how are they eliminated? (Include: long chain fatty acids; short chain fatty acids; chylomicrons; IDL; LDL; HDL; VLDL; cholesterol; bile; krebs cycle) 41) Trace, in detail, lactose through the GI tract to eventually be stored as glycogen in skeletal muscle fibers. 42) Trace a dipeptide through the GI tract to its eventually delivery to a skeletal muscle fiber, and then its degradation for ATP. 43) Draw a diagram inter-relating these processes and molecules: -glucose -glycogen -glycogenesis -glycogenolysis -glycolysis -pyruvic acid -gluconeogensis 44) Trace the elimination of NH4 (ammonia) from an amino acid in the blood to its eventual excretion as urea. 45) List the fat soluble vitamins.