* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Notes
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
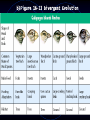
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
I. Background A. Charles Darwin 1. Born on February 12, 1809, same as Abraham Lincoln. 2. Sailed around the world on the HMS Beagle. 3. Made observations that led to the theory of evolution 4. Wrote Origin of Species. B. Galapagos islands 1. ¾ the size of the Hawaiian Islands. 2. Each island has a different climate. 3. About 625 miles off west coast of South America. 1 II. Evolution – process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. A. Natural selection: 1. Individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully. 2. Also called survival of the fittest. 3. Ex: Arctic hares hair color white (dom) vs. brown (rec) • Which allele will show up the most? • Which organism has a higher chance of survival in the arctic? 2 B. Natural selection vs. selective breeding 1. Natural selection allows nature to decide which traits are past to the offspring. a)Predator-prey relationship determines this. (fastest, strongest survive) 2. Selective breeding – allowing certain individuals with desired characteristics to produce the next generation. a)Ex: farmers want fattest hogs, cows that produce the most milk, reddest tomatoes, etc. b)Traits benefit humans, not nature. 3 C. Homologous structures – structures that have different mature forms but develop from the same embryonic tissues. 1. Figure 15-15, page 384. 4 2. Darwin concluded that homologous structures show common ancestry. 3. Functions may be different when mature (fin vs. wing), but look similar at the embryonic stage of development. D. Divergent vs. Convergent Evolution 1. Divergent evolution – process of 2 or more related species becoming more and more different. a)Diverge = separate 5 b)Figure 16-13 Divergent Evolution 6 2. Convergent evolution – unrelated species become more and more similar in appearance as they adapt in the same kind of environment. a)Converge = come together b)Figure 17-23 Shark, penguin, dolphin 7 III.Fossil record A. Fossil – any preserved part or trace of an organism that once lived. 1. Formed when organism is buried before it decays. 2. Found in sedimentary rock (layers of mud, silt, and sand on top of it). B. Determining the age of a fossil 1. Age is determined by the location in rock. a) Fossils closest to the surface are “newer” than those deeper. 8 b)Figure 17-3 page 419 9 2. Radioactive dating: a)Half-life – time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay. b)Carbon-14: 1)Half-life is 5,730 years. 2)Used for younger fossils. c)Uranium-238: 1)Half-life is 4.5 billion years. 2)Used for older fossils. 10