* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch.15 Notes - Green Local Schools
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
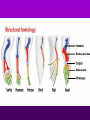
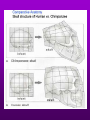
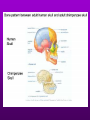
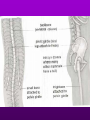
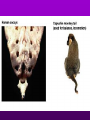
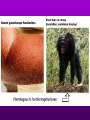
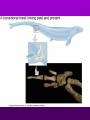
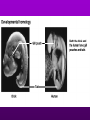
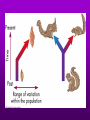
Theory of Evolution Ch. 15 (15-1) Evolution • Change of organisms over generations w/ a strong natural modification process • “Change over time” Scientific Theories • Explain data • Generations of predictions • Falsifiable Lamarck’s Theory • Use & Disuse: parts of body that are used extensively become larger & stronger while those that are not used deteriorate – Acquired traits Lamarck (cont.) • Ex: – Webbed foot = stretching of membrane b/w toes (water birds) • 1st to say: – Organisms change over time – New organisms are modified descendants of older types Darwin & Wallace’s Theory • Natural Selection: organisms best suited to their environment reproduce more successfully than others • “Survival of the fittest” Charles Darwin’s • Voyage on the Beagle Darwin’s Studying Ground Darwin’s Observations • 13 similar but separate species of finches – Specialized for food • Similarities lead to belief of a common ancestor Darwin’s Conclusions 1. Descent w/ modification 2. Modification by natural selection Descent w/ Modification • Newer species are modified descendants of older species • All species descended from 1 of a few original types of life Modification by Natural Selection • How evolution occurs • Environment limits pop.’s growth • Not all individuals in a pop. are identical & environment affects them differently Natural Selection (cont.) • Individuals w/ favorable traits reproduce more often than those w/ unfavorable traits • Thus favorable traits will be passed down more often Adaptation • Inherited trait that inc. an organism’s chance of survival in a particular environment – Based on genes Fitness • Ability to survive to propagate their genes (have babies) Lamarck vs. Darwin (15-2) Evidence of Evolution 1. Biogeography • Geographical distribution of species 2. Fossil Record • Type & order of fossils Evidence (cont.) 3. Homologous structures • Similar b/c of common ancestry 4. Comparative embryology • Study of structures that appear during embryonic development 5. Molecular biology • DNA & proteins Biogeography • New organisms arise in same geographic area where similar forms already lived • Ex: kangaroos only in Australia Fossil Record • Fossils: impressions of organisms from the past mineralized in rock • Links b/w modern forms & ancestors Distribution of Fossils • Law of superposition: lowest layers of rock are oldest • Fossil-bearing strata show when organisms became extinct • Mass extinction: brief period in which large #’s of species disappeared Homologous Structures • May have different functions but have similar anatomy • Shows a common ancestor • Ex: bird beaks & forelimbs Common Ancestor Analogous Structures • Similar look & function, but different embryological development & anatomy • Ex: bird & insect wings Vestigial Structure • Part of an organism w/ little or no function, but had a function in an ancestral species • Ex: human tailbone & appendix Comparative Embryology • All vertebrate embryos go through a stage in which they have gill pouches & tails Molecular Biology • The more similar the sequence, the more closely related 2 species are to each other • DNA, RNA, proteins (amino acids) Amino Acid Chart (15-3) Patterns of Evolution 1. Coevolution 2. Convergent Evolution 3. Divergent Evolution • Pattern & speed result from changes in the environment Coevolution • Change of 2 or more species in close association w/ each other • Ex: – Predator-prey – Parasite-host – Plant-animal pollinator Convergent Evolution • Organisms appear to be similar but are not closely related • Environment selects similar phenotypes • Ex: shark & porpoise Divergent Evolution • 2 or more related populations become more dissimilar in response to different habitats • Adaptive radiation – Galapagos finches • Artificial selection – Domestic dogs Divergent evolution of Grand Canyon squirrels Peppered Moth Evolution