* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
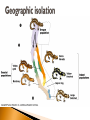
served on the HMS Beagle that sailed on a 5 year expedition his job was to collect, study, and store biological specimens ◦one of the locations was the Galapagos Islands, west of South America Darwin collected many species of finch he hypothesized that a few birds migrated from the mainland and adapted to the different island environments 1. Hutton and Lyell ◦ came up with the idea of gradualism, which explains how it took long periods of time to produce geographical features Jean Baptiste Lamarck ◦ one of the first scientists to recognize that living things have changed over time 2. 1. 2. 3. all organisms continually change in order to reach perfection organisms can alter their bodies by the principle of use and disuse he claimed that acquired characteristics could be inherited Thomas Malthus ◦ he stated in his essay The Principle of Population that if the human population continued to grow, sooner or later there would not be enough resources for everyone 3. Artificial selection (please add) ◦ Darwin observed how humans could change organisms by selection of specific traits 4. Darwin was forced to publish when another scientist, Alfred Wallace, came up with a similar idea Darwin’s book, Origin of Species, stirred up controversy for the next decade Natural Selection 1. not all individuals survive when competing for resources (“struggle for existence”) the individuals who survive are best adapted to their environment (“survival of the fittest”) ◦ nature acts on the variation within a population 2. 3. after many generations, the population may change to resemble the best adapted individuals (“descent with modification”) 1. Fossils ◦ there should be intermediate stages found in the fossil record Anatomy ◦ homologous structures are modified structures that show common ancestry 2. same on inside, different on outside ◦ analogous structures are different in arrangement but have a similar function different on inside, same on outside ◦ vestigial structures have no current purpose, but may have functioned in an ancestor Embryology ◦ similarities in embryo structure suggest evolution from a common ancestor 3. Biochemistry ◦ DNA or amino acid sequences can be compared to see how closely related 2 species are 4. Concealing coloration. Disruptive Coloration Disguises Counter shading Mimicry Select one type of camouflage. Color/shade it just right. Place it in it’s habitat! variation is the inheritable differences within the same species the gene pool is all of the genes present in a population changes in the frequencies of alleles is microevolution a population is the smallest unit that can evolve ◦ 1. mutation DNA 2. genetic - a permanent change in drift – chance events can change the gene pools of small populations 3. 4. 5. migration of individuals into and/or out of a population can change allele frequencies non-random mating (similar to selective breeding; only certain traits are desired) natural selection stabilizing selection ◦favors average individuals in a population 1. directional selection ◦favors one of the extreme forms of a trait 2. disruptive selection ◦individuals of both extreme forms are favored over the average 3. - a species is a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring Geographic isolation ◦ a physical barrier separates a population into groups (organisms adapt to their isolated environment) 1. Reproductive Isolation ◦ Occurs when organisms are prevented from producing fertile offspring occurs when mating behaviors/ times/seasons don’t match occurs when genetics aren’t similar enough 2. mass extinctions have wiped out a large number of Earth’s history Following these mass extinctions new species arise 1. Darwin proposed that evolution was a slow, steady process small adaptive changes accumulate over time this idea is known as gradualism punctuated equilibrium states that speciation occurs in relatively quick bursts ◦ The bursts of change are then followed by long periods of stability 2. divergent evolution is the pattern of evolution in which many different species can be traced back to a common (same) ancestor ◦ the different species adapted to different environments ◦ this is also called adaptive radiation 1. Evolution often happens among island chains because there are different habitats 2. convergent evolution occurs when distantly related organisms evolve similar traits