* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test Review Guide ch. 7, 9, 10
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
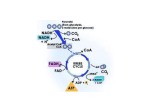
AP Biology – Test Review – Ch. 7, 9, 10 C. Gray Mitchell This is not an exhaustive list and not intended to be used as your only study resource. This is merely a guide to help you target essential topics and concepts. Membranes Plasma membrane structure - fluid mosaic model amphipathic phosphlipid bilayer structure carrier proteins integrated into membrane - structure semipermeable fully define: diffusion, osmosis, dialysis facilitated diffusion active transport cotransport and examples pinocytosis phagocytosis plasmolysis water potential (theory & calculations) hyper, hypo, isotonic solutions ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS Laws of Thermodynamics energy conversions/coupling entropy enthalpy free energy exergonic endergonic energy + ADP + Pi ATP List the three main stages of glucose oxidation in heterotrophs. 1. What type of molecule is ATP? 2. What is the final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration? 3. Where do glycolytic reactions occur? 4. Name the reactant molecules needed in glycolysis. What molecules are products? 5. Which enzyme supplies the activation energy for glycolysis? 6. What is the net ATP yield of glycolysis? 7. At what product is glycolysis completed? 8. Where does carbon oxidation occur? 9. Name three different carbon products made from pyruvate 10. The first chemical reaction in the Krebs cycle is ____ 11. The final energy products (and number) of each turn of the Krebs Cycle. 12.How many NADHS, FADH2, ATP are produced in the Krebs cycle? 13. Where is phosphorylation reaction substrate level or oxidative? 15. List three characteristics of the proton gradient in the inner matrix. 16. FADH2 and the NADH produced during glycolysis are similar because_____ 17. What is lactic acid respiration? Is it an arerobic or an anaerobic process? When does it occur? In what cell types? 18. Give the reaction(s) for alcoholic fermentation (starting with pyruvate). Why is this pathway needed by yeast? 19. What subatomic particles are added to NAD+ to reduce it to NADH? 21. Where are the molecules of the electron transport chain located? 22. How many ATP's does one completely oxidized glucose molecule produce in a typical eukaryotic cell? 23. What is the function of the ATP synthase complex? 24. What is the last reaction at the end of the cytochrome pathway in oxidative phosphorylation? 25. What is the difference between oxidative phosphorylation and substrate level phosphorylation? Where do each occur? 26. Which compounds get reduced, which get oxidized, when & where this happens. 27. Oxidizing and reducing agents. LABS: Diffusion/Osmosis lab w/ dialysis tubing and glucose/starch using IKI as indicator, Plant cell osmolarity determination, How to identify a series of solutions with unknown concentrations using principles of osmosis, rates of photosynthesis Cell respiration virtual labs on The Biology Place. Photosynthesis Review 1. light wavelengths: a. which are used by PS b. relative energy values of different colors c. absorption spectra of chlorophyll d. which color(s) is(are) reflected by green leaves 2. Chloroplast structure a. thylakoid b. stroma c. thylakoid membrane 3. The events in the light reactions, in chronological order 4. Water vapor from the air is split into H and O during Light reactions 5. H2O is the source of hydrogen and electrons to power chemiosmosis 6. Optimal wavelengths of the reaction centres in PS II and PSI. 7. The chemiosmotic process which results in the synthesis of ATP a. the source of energy to move protons b. where the proton gradient is c. where the ATP is synthesized 8. The differences between cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation 9. The reactant molecules needed for the Calvin cycle 10. The output of the Calvin Cycle is glyceraldehyde phosphate (G3P); this can be converted into fructose, dextrose, etc. 11. First step of Calvin Cycle and first intermediate. What is recycled? 12. What is oxidized & reduced. 13. Accounting of NADPH, ATP.