* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
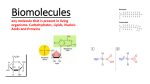
Download any molecule that is present in living organisms. Carbohydrates
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biomolecules any molecule that is present in living organisms. Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids and Proteins Biomolecules • Warm-up • List the percentages of each: • Total Fats ____ • Saturated Fats ____ • Carbohydrates _______ • Protein ____ • What Biomolecule would cholesterol be classified as? _____________ 4 Classes of Organic Compounds All Contain Carbon Monomers (M) (Building Blocks) (Building Blocks Macromolecules CHO CHONP Carbohydrates Nucleic Acids M=Sugars M= Nucleotides starch es DNA cellulose RNA glycogen CHONS CHO Lipids M= Fatty Acids and Glycerol Proteins M= Amino Acids fats enzymes oils muscle fibers waxes cytoskeleton steroids Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 1 Levels of organization Macromolecule Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, found in food help make me along with nucleic acids!!!! Monomer vs Polymer Monomer-single unit Polymer: many single units joined together Dehydration Synthesis: removing water to form polymers Hydrolysis: adding water to break down into monomers C H O 1: 2: 1 Main source of energy, especially short term energy Monomer: Sugar Monosaccharide: simple sugar Used for genetic material, which codes for traits Monomer: Nucleotide CHONP DNA: A C G T RNA: A G C U Disaccharide: double (two) sugars Polysaccharide: many (large) sugars Carbohydrates Glucose, Nucleic Acids DNA, RNA, ATP Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen Macromolecules Lipids Proteins Fats, Oils, Enzymes, Waxes Cell structure Saturated: only C-C single bonds Unsaturated: at least 1 C = C double bond Triglyceride: 3 fatty acids + glycerol CHO Monomer: Triglyceride Bonded by: Peptide Bonds Used for long term energy storage Used for antibodies, muscle movement, enzymes, hormones, structure, transport, and to store amino acids Monomer: Amino Acid C H O N (S) Crash Course Biomolecules Enzymes: Are Proteins Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions No living organism can Function WITHOUT Enzymes Enzymes: 1. 2. 3. 4. Build molecules: Synthesis Enzymes Break Down Molecules: Digestive enzymes Speed up reactions: Catalysts Lowers activation energy: Lock and Key Theory Each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job. Can affect the enzyme action. 1. Temperature 2. pH If the temp. and pH is to extreme the enzyme will denature. Denature: permanently change the shape of the enzyme. Will no longer work Enzymes are proteins • Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction • enzymes are named for the reaction they help • • • • Oh, I get it! They end in -ase sucrase breaks down sucrose proteases breakdown proteins lipases breakdown lipids DNA polymerase builds DNA