* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
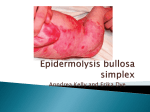
Download Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex in IsraelClinical and Genetic Features
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
From: Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex in IsraelClinical and Genetic Features Arch Dermatol. 2003;139(4):498-505. doi:10.1001/archderm.139.4.498 Figure Legend: Distribution of the mutations found in 8 Israeli families with epidermolysis bullosa simplex along K5 and K14 keratin molecules. Date of download: 8/3/2017 Copyright © 2003 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. From: Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex in IsraelClinical and Genetic Features Arch Dermatol. 2003;139(4):498-505. doi:10.1001/archderm.139.4.498 Figure Legend: Mutation analysis in family 1. A, DNA sequence of part of K14 exon 6 in the proband (upper panel), his father (middle panel), and an unrelated individual (lower panel). Direct sequencing of the patient's polymerase chain reaction product (upper panel) revealed a homozygous C→T transition at complementary DNA position 1186, resulting in the substitution of a glutamine residue at amino acid position 396 by a stop codon. The father of the patient carries the mutation in a heterozygous state (middle panel). B, Electron microscopic examination of skin biopsy specimen obtained from American the affected child. Tonofilaments are present in the suprabasal cells Copyright © 2003 Medical Date (SB) of butdownload: not within8/3/2017 basal cells (B) (original magnification ×2000). C, Immunohistochemical staining of a biopsy specimen taken from Association. All rights reserved. the proband of family 1 (Q396X/Q396X) and from a healthy control (WT/WT) using a monoclonal antibody directed against K14. From: Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex in IsraelClinical and Genetic Features Arch Dermatol. 2003;139(4):498-505. doi:10.1001/archderm.139.4.498 Figure Legend: Mutation analysis in family 4. A, DNA sequence of K14 exon 6 in an affected child (upper panel), her mother (middle panel), and her father (lower panel). The R388H and Q396X mutation sites are marked with an arrow. B, Polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism confirmation of the R388H mutation and pedigree of the family. Squares indicate male individuals and circles indicate female individuals. Black symbols represent affected individuals. To verify R388H, a 1460–base pair (bp) polymerase chain reaction fragment was amplified from family members' DNAAmerican and digested with DNA endonuclease TspRI. R388H creates a Copyright © 2003 Medical Date download: site 8/3/2017 novelofrecognition for TspRI, which leads to theAssociation. generationAll of rights a 652-bp fragment, present only in carriers of the mutation. reserved. Accordingly, the 2 patients (lanes 3 and 4) and their father (lane 1) displays a 652-bp fragment that is absent in 2 healthy children