* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name___________________________ Lab #______ Role: Activity
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
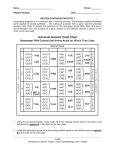
Name___________________________ Lab #____________ Role: _________________ Activity 1. Protein Synthesis In this activity, you will model the steps of protein synthesis. Before beginning, your group should have: 20 amino acid links each labeled as a different amino acid 30 pop beads of each color 30 connector pieces mRNA Codons for Amino Acids chart colored pencils Key: Adenine—red pop bead Thymine—yellow pop bead Guanine—blue pop bead Cytosine—purple pop bead Uracil—orange pop bead Hydrogen bonds—clear connectors 1. Working in groups of three, build a DNA strand with pop beads using the key provided. (Note: This does not represent an actual DNA sequence, the DNA sequence is used for demonstration purposes only). Build the DNA strand using the order of nucleotides in the diagram below. Your DNA strand will be 25 bases long. Color the diagram below according to the key, using colored pencils. NOTE: Replication is not a part of protein synthesis but will be demonstrated here for practice. 2. Practice replication by copying the above DNA strand to form a complementary DNA strand. Use the clear connectors to form “bonds” between complementary nucleotide bases by inserting the connector into the bottom of the original DNA nucleotide base and the top of the replicated DNA nucleotide base. Fill in the replicated DNA strand below with each nucleotide and color using colored pencils according to the key. When you have completed your strand, you will have a DNA double strand. Twist the two strands to create a double helix. Replicated DNA Strand 3. Once your replicated strand has been checked by your teacher, separate the two strands and set aside the original strand. Transcribe the replicated DNA strand into an mRNA strand. Use the same process for connecting the DNA and mRNA strands as was followed in Step 2. Record the transcribed mRNA strand below and color it accordingly. mRNA 4. Using the transcribed mRNA strand, begin the process of translation. You will need the mRNA Codons for Amino Acids chart and the amino acid links that you labeled before you began the lab. Set the links off to the side. Begin translation by locating the start codon on the mRNA strand. 5. You will now use the pop beads to create a tRNA molecule that is complementary to the start codon. Connect the three complementary beads to one another. 6. Once the complementary tRNA anticodon is in place, determine the appropriate amino acid by using the chart. Retrieve the correct amino acid link and bring both the tRNA and amino acid back to the mRNA strand. Attach the tRNA and lay the amino acid above the tRNA strand. This amino acid link will be the beginning of your protein chain. Name___________________________ Lab #____________ Role: _________________ 7. After the first amino acid is in place, locate the next codon. Assemble the complementary tRNA anticodon and repeat Step 6. 8. After the second amino acid link is brought to the mRNA strand, begin forming the protein chain by separating the amino acids from the tRNA and linking them together, as shown. 9. [Type a quote from the document or the summary of an interesting point. You can position the text box anywhere in the document. Use the Drawing Tools tab to change the formatting of the pull quote text box.] Continue building the protein chain by locating amino acids and making tRNA anticodons and bringing the anticodons and amino acids to the mRNA to connect the amino acids together to form a chain. Your protein chain will be complete when you reach the stop codon. There is no amino acid associated with the stop codon. 10. When your chain is complete, record the amino acids in order from the start codon to the stop codon on the diagram below. 11. Have your teacher check your protein chain. Then, disassemble all strands and amino acid links except for the original DNA strand. Save this strand for Activity 2. Activity 2. Genetic Mutation You and your group will design an experiment to observe the effects that changes in DNA have on proteins. You will need: 30 pop beads of each color 30 connector pieces 20 amino acid links w/ labels 3 amino acid links w/ blank labels 1. 3. For this activity, you will use the original DNA strand from Activity 1. The strand should look like the diagram below: 2. With your group, brainstorm ways that this DNA strand could be altered. List some examples here: Choose one of the changes that you listed in Step 2 to experiment with. Explain below how you will alter the DNA strand & make these changes on your DNA model. If you need additional pop beads, I will supply them for you. Record the altered DNA strand on the following diagram. Note: Beads have been added to the diagram. If you remove beads, simply mark them off of your strand with an X. Altered DNA Strand Name___________________________ Lab #____________ Role: _________________ 4. Record a prediction of how you expect to the change in DNA will affect the protein at the end of protein synthesis. Prediction: 5. Complete the steps of protein synthesis from Activity 1 with the altered DNA strand from Step 3. Begin with transcribing the altered DNA into mRNA. Record the mRNA strand below. (Note: Cross off any beads you do not use with an X.) 6. After completing the steps of translation from Activity 1, label the amino acids (if any exist) from the completed protein chain on the diagram below. (Note: Cross of any links you don’t use with an X.) 7. Take note of the changes that took place in protein synthesis due to the altering of the DNA strand. Describe the changes that occurred in the protein. 8. Go the board and write out your original chain, type of mutation, and the resulting protein chain. We will compare the class results at the end. Put all of your supplies away neatly and push in your stools. Go back to your desks and wait patiently for everyone to finish.