* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELLS
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
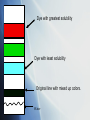
CELLS Building Blocks of Life Every living thing is made of cells Cells complete different functions in different parts of organisms. Muscle cells help us move Fat cells store energy Form and Function Cells have different sizes, shapes and parts. Their appearance will reflect their function. Cells Shapes Plant cells are usually rectangular because of their thick cell wall. Animal cells are usually rounded because they lack cell walls. Cell Shape Pictures The Two Cell Types Prokaryotic Simple cells no complex organelles Small cells average size 1 micrometer Bacteria only example Oldest known form of life The Two Cell Types Eukaryotic: Complex cells many organelles Large cells average 20 micrometers Plants, animals, fungi, protists, Evolved much later than prokaryotic cells Cell Parts Cell Membrane: Thin covering on outside of the cell. Controls movement of materials into & out of the cell. needed materials wastes Cell Wall Thick, strong covering on the outside of plant cells only. Provides protection & support for the plant. Plan Cell Diagram Cytoplasm Jelly-like material in the cell Contains the organelles. Organelle (small organ) A structure in the cytoplasm that performs a specific function. Organelles Nucleus: The control center of the cell. Contains the cell’s genetic material in the DNA molecule Nucleolus Found inside nucleus Produces ribosome Chromosomes Found inside nucleus Contain DNA Holds the cells ‘blue prints” Contain the cells genetic information Ribosomes The cell’s protein factory Endoplasmic Reticulum: Series of membranes used to transport materials through the cytoplasm. Mitochondria Hot dog shape with many folds organelle where sugar is converted to usable energy. Cells can have many mitochondria Site of cell respiration. C Chloroplasts Site of photosyntheisis Captures sun’s energy to make food Green, oval organelle Contains chlorophyll Makes leaves green Photosynthesis sunlight 6CO2 +6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 CHROMOPLASTS Same function as chloroplasts They use different wavelengths of light. Contain the bright pigments that give Fall leaves their colors LEUCOPLASTS Used in starch storage: We will see them in potato cells. Golgi Body Flat sacs, look like stack of records Used to wrap materials so that they can easily be transported out of the cell Makes lysosomes DIFFUSION & OSMOSIS Diffusion The gradual spreading of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lesser concentration. Examples Smoke spreading in air Salt spreading in water Water spreading through a paper towel Osmosis The diffusion of water into or out of cells Examples Cells placed in salt water shrink Cells placed in fresh water grow CHROMATOGRAPHY Chromatography: A technique used to separate materials based on differing chemical or physical properties. Paper Chromatography: The type of chromatography we used to separate dyes based on their solubility in water. Solubility: Describes how easily one substance dissolves in another. CHROMATOGRAPHY The dye with the greatest solubility will travel the furthest up the filter paper. The dye with the least solubility will travel the shortest distance up the filter paper. CHROMATOGRAPHY Other types of chromatography are used to separate other materials. For example gel chromatography is used to separate DNA molecules. Dye with greatest solubility Dye with least solubility Original line with mixed up colors. Water