* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hauger Climate security
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Myron Ebell wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Australia wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
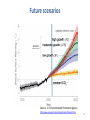
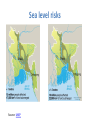
J. Scott Hauger, Ph.D., Asia-Pacific Center for Security Studies Pacific Operational Science & Technology Conference Honolulu, HI March 5, 2013 “Climate change has the potential for significant impacts on all three of the basic elements important to national and international security – defense, diplomacy, and economics…. The most immediate effects with the highest potential for instability will come from the most vulnerable regions of the world where the United States obtains vital fuel and strategic mineral imports and combats terrorism.” “Trends and Implications of Climate Change for National & International Security, “U.S. Defense Science Board. Oct 2011, p. xiii. 2 Outline 1. Science of climate change. 2. Climate change and security. 3. Security dimensions of climate change in the Asia-Pacific Region. 4. Science & Technology for Climate Related Security 5. Conclusion: Challenges & Opportunities 3 Outline 1. Science of climate change. 2. Climate change and security. 3. Security dimensions of climate change in the Asia-Pacific Region. 4. Science & Technology for Climate Related Security 5. Conclusion: Challenges & Opportunities 4 Global warming is an observed fact. Source: U.S. NASA. March 9, 2012. Available at: http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp/graphs_v3/ 5 The greenhouse effect 6 Measured atmospheric CO2 Source: U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration 7 Future scenarios Source: U.S Environmental Protection Agency http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/futuretc.html 8 Outline 1. Science of climate change. 2. Climate change and security. 3. Security dimensions of climate change in the Asia-Pacific Region. 4. Science & Technology for Climate Related Security 5. Conclusion: Challenges & Opportunities 9 Climate change and security Climate Effects Human Impacts State Impacts •Rising sea levels •Freshwater •Conflict over: •Tropical cyclones •Food production •More floods •Disease •More droughts •Migration •Riverine erosion •Infrastructure •Blame •Frame •Resources •Migration •Maritime boundaries •Increased stress on weak governments 10 Outline 1. Science of climate change. 2. Climate change and security. 3. Security dimensions of climate change in the Asia-Pacific Region. 4. U.S. policy for science & climate change. 5. Conclusion: Challenges & Opportunities 11 Drought risk indicators, 2030-2040 Based on current global climate models and IPCC A1B emissions scenario. Source: CARE International Climate Change Information Centre 12 Flood risk indicators, 2030-2040 Based on current global climate models and IPCC A1B emissions scenario. Source: CARE International Climate Change Information Centre 13 Cyclone risk indicators, 2030-2040 Based on current global climate models and IPCC A1B emissions scenario. Source: CARE International Climate Change Information Centre 14 Sea level risks Source: UNEP Migration Image source: Lisa Friedman. “Bangladesh: Where the Climate Exodus Begins” “In 2010, more than 30 million people in Asia and the Pacific were displaced by environmental disasters such as storms and floods... Climate change is expected to increase the frequency of extreme weather events, bringing about significant changes in migration patterns. This will pose a major threat to the growth and security of Asia and the Pacific unless measures are taken soon. ” -- Asian Development Bank. 15 Sep, 2011 16 U.S. security policy QDR 2010 “…climate change could have significant geopolitical impacts around the world, contributing to poverty, environmental degradation, and the further weakening of fragile governments. Climate change will contribute to food and water scarcity, will increase the spread of disease, and may spur or exacerbate mass migration…. In some nations, the military is the only institution with the capacity to respond to a large-scale natural disaster. Proactive engagement with these countries can help build their capability to respond to such events.” Source: U.S. DoD. 2010. Quadrennial Defense Review. (February), pp. 845. Available at: http://www.defense.gov/Q DR/ 17 Outline 1. Science of climate change. 2. Climate change and security. 3. Security dimensions of climate change in the Asia-Pacific Region. 4. Science & Technology for Climate Related Security 5. Conclusion: Challenges & Opportunities 18 Mission: To build a knowledge base that informs human responses to climate and global change through coordinated and integrated federal programs of research, education, communication, and decision support USGCRP Strategic Plan 2012- 2021 • Shift from climate change perspective to one of climate-related global changes. • Better integrate social and ecological sciences to inform decisions. • Build an integrated observational system that connects observations of the physical environment with social and ecological observations. 21 Defense Science Board report (Oct 2011) U.S. DoD needs: • Comprehensive climate information system to support operational assessments. • To develop local expertise in civil engineering, hydrology, energy, agriculture, land use & Infrastructure planning so developing nations can benefit from information. • Better processes to coordinate & leverage U.S. agency efforts. • Better insights into activities of other countries & international organizations. DSB Findings: Role for DoD • Build regional capabilities and alliances to create climate change resilience. • Prepare to respond to natural disasters. • Assist foreign militaries to understand climate change effects on force structure, installations, and security situation. • Build capacity for mitigation & adaptation. DSB Findings: Role for COCOMs • Identify regional early warning indicators. • Include energy, food, water & disaster risk reductions strategies in theater campaign plan. • Conduct regional / local impact assessments. • Include as Tier 1 objective, enhancing host nation military and civil readiness groups to respond to natural disasters. • Integrate climate-change related aspects into exercises. National Research Council Findings • Expect increasingly more serious climate surprises in the coming decade. • It is essential for the intelligence community to understand adaptation and changes to vulnerability to climate events. • Prudent to expect some climate events that exceed the capacity of affected societies to manage. NRC Recommendations • Research to improve ability to quantify likelihoods of climate events. • Intelligence community should provide appropriate research support. • Research needed to understand when climate disasters do/don’t lead to security-relevant outcomes. NRC Recommendations (2) • Immediately begin a WoG strategy for monitoring threats connected to climate change. • “Stress test” countries, regions & global systems for ability to manage disruptive climate events. – Focus on critical watershed areas in South Asia, Middle East & Africa Outline 1. Science of climate change. 2. Climate change and security. 3. Security dimensions of climate change in the Asia-Pacific Region. 4. Science & Technology for Climate Related Security 5. Conclusion: Challenges & Opportunities 28 Conclusion: Challenges & Opportunities (1) • Anticipate climate-related surprises. • Need for a DoD / U.S. / regional observation system for relating climate change to security threats. • Corresponding need for methodologies that integrate social & ecological sciences for threat characterization & prediction • Impact assessments & “Stress tests” using new data and knowledge to develop an ability to manage disruptive climate events. Conclusion: Challenges & Opportunities (2) • Develop local expertise in Asia Pacific region in civil engineering, hydrology, energy, agriculture, land use & infrastructure planning so developing nations can benefit. • Develop processes to coordinate & leverage U.S. agency efforts. • Regional security structure development for information sharing, planning and response. QUESTIONS? Image source: Risk Management Monitor 31