* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
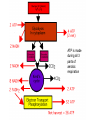
CELLULAR RESPIRATION Energy in Food To do work, cells require energy One gram of glucose contains 3811 calories A calorie is defined as the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius Food labels use the kilocalorie or Calorie which is actually 1000 calories Cellular Respiration Process by which glucose is broken down to produce energy (ATP) The cellular respiration reaction is: energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 6H2O + 6CO2 There are two types of cellular respiration: Aerobic Anaerobic Aerobic Respiration There are 3 steps in aerobic respiration: Glycolysis Krebs cycle Electron transport Glycolysis Glucose is broken down to produce 2 molecules of pyruvic acid (a.k.a. pyruvate) and the energy carriers ATP and NADH These reactions occur in the cytoplasm 2ATP glucose 2ADP 4ADP 2PGAL 2NAD+ 4ATP 2 pyruvic acid 2NADH + 2H+ Krebs Cycle (a.k.a. Citric Acid Cycle) The pyruvic acid made during glycolysis is converted into citric acid The citric acid enters the Krebs cycle and is converted into carbon dioxide (a waste product), ATP, NADH, and FADH2 The NADH and FADH2 can now enter the electron transport chain These reactions take place in the mitochondria Electron Transport NADH and FADH2 are put through the chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ATP is made during all 3 parts of aerobic respiration Anaerobic Respiration The extraction of energy from pyruvic acid in the absence of oxygen This is also known as fermentation The process begins with glycolysis to produce pyruvic acid There are 2 types: Alcoholic fermentation Lactic acid fermentation Alcoholic Fermentation pyruvic acid + NADH CO2 + ethanol + NAD+ This reaction occurs mainly in yeast cells Used to make bread as well as alcoholic beverages Lactic Acid Fermentation pyruvic acid + NADH lactic acid + NAD+ This reaction occurs in muscle cells and it is the build up of lactic acid that causes muscle soreness Excess Glucose Excess glucose can be stored Animal cells store it as glycogen or fat