* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download By what process do most stars release energy? A. Electromagnetic
Nuclear fission wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion–fission hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Fallout shelter wikipedia , lookup
Background radiation wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission product wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive waste wikipedia , lookup
Gamma spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Muon-catalyzed fusion wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Inertial electrostatic confinement wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive decay wikipedia , lookup
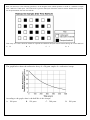
By what process do most stars release energy? A. Electromagnetic induction resulting from strong magnetic elds B. Radioactivity in the interior of the star C. Nuclear fusion in the interior of the star D. Heat which was stored when the star was 'born' Carbon-14 has a half-life of approximately 5,700 years. Analysis of the carbon in a piece of charred wood found in an excavation revealed that the carbon has 25 percent of the amount of carbon-14 that is found in the carbon of living trees. Which of the following is most nearly the age of the excavated wood? A. 160 years B. 5,700 years C. 11,400 years D. 23,000 years Nuclear energy can be generated by ssion or fusion. Fusion is not currently being used in reactors as an energy source. Why is this? A. The scienti c principles on which fusion is based are not yet known. B. The technological processes for using fusion safely are not developed. C. The necessary raw materials are not readily available. D. Waste products from the fusion process are too dangerous. The nal elements produced by radioactive decay di er from the original radioactive elements because the nuclei of the nal elements are always A. more stable. B. increased in mass. C. half as radioactive. D. positively charged. The three main types of nuclear radiation are alpha, beta, and gamma. Which of the following lists these types of radiation from highest penetrating power to lowest penetrating power? A. alpha, gamma, beta B. beta, alpha, gamma C. beta, gamma, alpha D. gamma, beta, alpha A hospital buys a compound that contains an isotope of barium. Several months later, most of the barium has changed to the element lanthanum. Which of the following is responsible for this change? A. exposure to air B. radioactive decay C. reactions with the container wall D. absorption of moisture from the air Which of the following statements best describes a di erence between nuclear ssion and nuclear fusion reactions? A. Nuclei split during ssion and combine during fusion. B. Fission forms heavier elements, and fusion forms lighter elements. C. Fission generates potential energy, and fusion generates kinetic energy. D. Nuclei gain electrons during ssion and release electrons during fusion. Which of the following statements describes a gamma ray? A. A gamma ray has no mass. B. A gamma ray has a positive charge. C. A gamma ray can be stopped by a sheet of paper. D. A gamma ray can be converted into a beta particle. The diagram below shows a radioactive isotope going through several half-lives as it decays. In sample I, the original isotope has a mass of 40 g. How many grams of the original isotope remain in sample IV? A. 37.5 g B. 20 g C. 10 g D. 5 g Great amounts energy are released in the core of a star as lighter elements combine and form heavier elements during the process of A. compaction B. condensation C. radioactive decay D. nuclear fusion Why are radioactive substances useful for measuring geologic time? A. The ratio of decay products to radioactive substances remains constant in rocks. B. The half-lives of radioactive substances are short. C. Samples of radioactive substances are easy to collect from rocks. D. Radioactive substances undergo decay at a predictable rate. The table below gives information about the radioactive decay of carbon-14. Part of the table has been deliberately left blank for student use. Half-life 0 Mass of Original Carbon-14 Number of Years Remaining (grams) 1 0 1 2 1 4 1 8 1 16 1 2 3 4 5 5,700 11,400 17,100 6 7 After how many years will A. 22,800 yr 1 128 B. gram of the original carbon-14 remain? 28,500 yr C. 34,200 yr D. 39,900 yr Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below, which represents a model of a radioactive sample with a half-life of 5000 years. The white boxes represent undecayed radioactive material and the shaded boxes represent the decayed material after the rst half-life. How many more boxes should be shaded to represent the additional decayed material formed during the second half-life? A. 12 B. 6 C. 3 D. 0 The graph below shows the radioactive decay of a 50-gram sample of a radioactive isotope. According to the graph, what is the half-life of this isotope? A. 100 years B. 150 years C. 200 years D. 300 years When a radioactive atom emits an alpha particle, the mass number of the atom A. decreases B. increases C. remains the same Neutrons are used to bombard heavy nuclei to form radioactive isotopes because they are A. attracted to the nucleus B. repelled by the electrons C. heavier than alpha particles D. not electrically charged The reaction 31 H + 21 H ! 42 He + 10 n + E illustrates the process of A. alpha decay B. ssion C. neutron bombardment D. fusion Which force between the protons in a helium atom will have the greatest magnitude? A. gravitational force B. electrostatic force C. nuclear force D. magnetic force Which statement best describes the ssion products from nuclear reactors? A. They are nonradioactive and may be safely discarded. B. They are nonradioactive and must be treated and/or stored. C. They are intensely radioactive and may be safely discarded. D. They are intensely radioactive and must be treated and/or stored. Compared to electrostatic forces, nuclear forces are A. weaker and of shorter range B. weaker and of longer range C. stronger and of shorter range D. stronger and of longer range