Integrated Science COS-Grade 9 2011 2012
... amount of energy. (Fission involves the splitting of a large nucleus into smaller nuclei; fusion is the joining of two small nuclei into a larger nucleus at extremely ...
... amount of energy. (Fission involves the splitting of a large nucleus into smaller nuclei; fusion is the joining of two small nuclei into a larger nucleus at extremely ...
EOCT Physical Science Atomic Theory
... B. the smallest of the three major particles. C. the same as the mass of the proton. D. the same as the mass of the atom. 37. What is the main problem in developing nuclear fusion as an efficient source of energy? A. The fuel needed is too expensive at this time. B. Dangerous gamma and neutron rays ...
... B. the smallest of the three major particles. C. the same as the mass of the proton. D. the same as the mass of the atom. 37. What is the main problem in developing nuclear fusion as an efficient source of energy? A. The fuel needed is too expensive at this time. B. Dangerous gamma and neutron rays ...
Atomic Number - Physical Science
... • Damage from alpha particles can cause cells not to function properly, leading to illness and disease • Some smoke detectors give off alpha particles to ionize the surrounding air • If smoke particles enter the ionized air, they will absorb the ions and electrons so the circuit is broken and the ...
... • Damage from alpha particles can cause cells not to function properly, leading to illness and disease • Some smoke detectors give off alpha particles to ionize the surrounding air • If smoke particles enter the ionized air, they will absorb the ions and electrons so the circuit is broken and the ...
Atomic Mass Unit and Isotopes
... are high speed helium nuclei with a +2 charge and fairly low penetrating power. Beta particles (β) – represented by 0-1β , are high speed electrons with a -1 charge and high penetrating power. Gamma rays (γ) – represented by 00γ , are high energy electromagnetic waves with no charge and extremely ...
... are high speed helium nuclei with a +2 charge and fairly low penetrating power. Beta particles (β) – represented by 0-1β , are high speed electrons with a -1 charge and high penetrating power. Gamma rays (γ) – represented by 00γ , are high energy electromagnetic waves with no charge and extremely ...
Nickel-Hydrogen Cold Fusion by Intermediate Rydberg State of
... mechanical (QM) models of atoms are based on the Rutherford-Bohr planetary model of hydrogen. The nuclear size is determined by scattering experiments, while the nuclear shape for all atoms is assumed spherical and solid (without geometrical shape and structure). Using this assumption Rutherford pro ...
... mechanical (QM) models of atoms are based on the Rutherford-Bohr planetary model of hydrogen. The nuclear size is determined by scattering experiments, while the nuclear shape for all atoms is assumed spherical and solid (without geometrical shape and structure). Using this assumption Rutherford pro ...
Fusion or Fission
... keep going is called the critical mass. The trouble with fission reactions is that radiation and nuclear waste products are created in the process. This is a problem, as many nuclear power plants use fission to produce energy, producing a lot of radioactive byproducts as a result. 4 Conversely, in f ...
... keep going is called the critical mass. The trouble with fission reactions is that radiation and nuclear waste products are created in the process. This is a problem, as many nuclear power plants use fission to produce energy, producing a lot of radioactive byproducts as a result. 4 Conversely, in f ...
Fission and Fusion Power Point
... by inserting CADMIUM RODS into the reaction chamber. These rods absorb some of the NEUTRONS produced and slow the CHAIN REACTION so that it can proceed at a CONTROLLED RATE. ...
... by inserting CADMIUM RODS into the reaction chamber. These rods absorb some of the NEUTRONS produced and slow the CHAIN REACTION so that it can proceed at a CONTROLLED RATE. ...
Static electricity
... g) We used to think that atoms were like a plumb pudding where the negative charges are trapped in a ‘pudding mixture of positive charge. h) The Rutherford and Marsden scattering experiment led to the plum pudding model of the atom being replaced by the nuclear model. Electrons were fired at a leaf ...
... g) We used to think that atoms were like a plumb pudding where the negative charges are trapped in a ‘pudding mixture of positive charge. h) The Rutherford and Marsden scattering experiment led to the plum pudding model of the atom being replaced by the nuclear model. Electrons were fired at a leaf ...
6.2 Atomic Nucleus Stability and Isotopes
... bound together in a formed nucleus is always less than the mass of the same number of protons and neutrons not yet bound together. The mass that protons and neutrons lose when they bind together into a nucleus is called the mass ...
... bound together in a formed nucleus is always less than the mass of the same number of protons and neutrons not yet bound together. The mass that protons and neutrons lose when they bind together into a nucleus is called the mass ...
TRENDS OR PATTERNS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE
... The 3s and 3p sublevels are removed thereby reducing the size of the electron cloud. The cation is also smaller than the atom because there is the same number of protons pulling on fewer electrons. A Li+ ion is smaller than the Li atom. The most metallic elements are the ones that lose electrons mos ...
... The 3s and 3p sublevels are removed thereby reducing the size of the electron cloud. The cation is also smaller than the atom because there is the same number of protons pulling on fewer electrons. A Li+ ion is smaller than the Li atom. The most metallic elements are the ones that lose electrons mos ...
CHAPTER 13: Nuclear Interactions and Applications
... Because neutrons have zero net charge, they interact more easily with nuclei at low energies than do charged particles, because of the Coulomb barrier. This process is called neutron activation and the reaction is called neutron radioactive transfer. The average neutron capture cross section (at ene ...
... Because neutrons have zero net charge, they interact more easily with nuclei at low energies than do charged particles, because of the Coulomb barrier. This process is called neutron activation and the reaction is called neutron radioactive transfer. The average neutron capture cross section (at ene ...
Chapter Terms - Jensen English Academy! (JEA)
... Nuclear Charge (pg. 171) Term given to electric charge on the nucleus. Simply count protons. The nuclear charge is the same as the ATOMIC NUMBER Atomic Number (pg. 171) Same as NUCLEAR CHARGE in a NEUTRAL ATOM Period (pg. 171) Used at the end of this sentence. Also, a left to right row on the period ...
... Nuclear Charge (pg. 171) Term given to electric charge on the nucleus. Simply count protons. The nuclear charge is the same as the ATOMIC NUMBER Atomic Number (pg. 171) Same as NUCLEAR CHARGE in a NEUTRAL ATOM Period (pg. 171) Used at the end of this sentence. Also, a left to right row on the period ...
Fission and Fusion
... In this example, a stray neutron strikes an atom of U-235. It absorbs the neutron and becomes an unstable atom of U-236. It then undergoes fission. Notice that more neutrons are released in the reaction. These neutrons can strike other U-235 atoms to initiate their fission. ...
... In this example, a stray neutron strikes an atom of U-235. It absorbs the neutron and becomes an unstable atom of U-236. It then undergoes fission. Notice that more neutrons are released in the reaction. These neutrons can strike other U-235 atoms to initiate their fission. ...
Notes: Nuclear Chemistry
... Emission of beta particles = the equivalent of an electron caused by the breaking down of a neutron into a proton and a fast-moving electron. The symbol for beta radiation is β- or 0-1e. It has moderate penetrating power and a -1 charge. Beta particles need thin sheets of metal (>3mm) to stop their ...
... Emission of beta particles = the equivalent of an electron caused by the breaking down of a neutron into a proton and a fast-moving electron. The symbol for beta radiation is β- or 0-1e. It has moderate penetrating power and a -1 charge. Beta particles need thin sheets of metal (>3mm) to stop their ...
Energy per nucleon
... • A balance between the production and decay rates determines the equilibrium ratio: ...
... • A balance between the production and decay rates determines the equilibrium ratio: ...
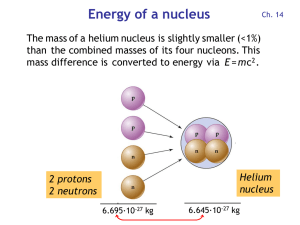
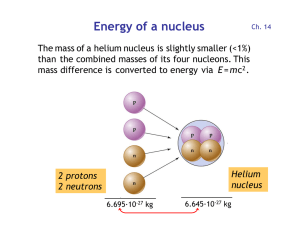
Energy of a nucleus
... • A balance between the production and decay rates determines the equilibrium ratio: ...
... • A balance between the production and decay rates determines the equilibrium ratio: ...
Atomic/Nuclear
... When an electron is released, a new nucleus is formed with one more protons and one less neutron. An anti neutrino is also released during beta decay. This is a chargeless, massless particle. Gamma rays are short bursts of very high frequency electromagnetic waves. When a gamma ray is released, the ...
... When an electron is released, a new nucleus is formed with one more protons and one less neutron. An anti neutrino is also released during beta decay. This is a chargeless, massless particle. Gamma rays are short bursts of very high frequency electromagnetic waves. When a gamma ray is released, the ...
Content Domain III: Chemistry—Atomic Theory and
... isotopes, law of conservation of matter, matter, neutron, nucleus, proton, alpha particles, beta particles, fission, fusion, gamma radiation, half-life, radioactive decay. The current model suggests that an atom consists of a positively charged, small, dense central region surrounded by a negatively ...
... isotopes, law of conservation of matter, matter, neutron, nucleus, proton, alpha particles, beta particles, fission, fusion, gamma radiation, half-life, radioactive decay. The current model suggests that an atom consists of a positively charged, small, dense central region surrounded by a negatively ...
Periodic Trends
... the atom, the more likely it is to attract an electron that is in a chemical bond. Atoms get smaller going left to right, so the nucleus is closer to the outside of the atom. ...
... the atom, the more likely it is to attract an electron that is in a chemical bond. Atoms get smaller going left to right, so the nucleus is closer to the outside of the atom. ...
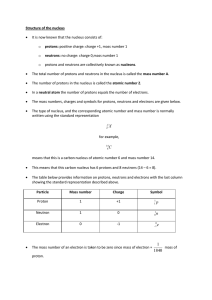
Structure of the nucleus • It is now known that the nucleus consists of
... The challenge is in heating the fuel to very high temperatures – and in confining the plasma within itself to prevent any plasma touching the walls of its container – any contact with the container results in cooling. ...
... The challenge is in heating the fuel to very high temperatures – and in confining the plasma within itself to prevent any plasma touching the walls of its container – any contact with the container results in cooling. ...
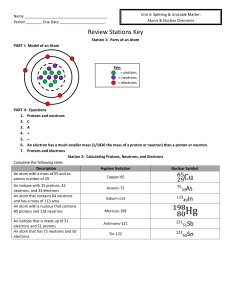
Name Period ______ Due Date Review Stations Key Station 1
... An isotope with 33 protons, 42 neutrons, and 33 electrons An atom that contains 64 neutrons and has a mass of 113 amu An atom with a nucleus that contains 80 protons and 118 neutrons An isotope that is made up of 51 electrons and 51 protons An atom that has 72 neutrons and 50 electrons ...
... An isotope with 33 protons, 42 neutrons, and 33 electrons An atom that contains 64 neutrons and has a mass of 113 amu An atom with a nucleus that contains 80 protons and 118 neutrons An isotope that is made up of 51 electrons and 51 protons An atom that has 72 neutrons and 50 electrons ...
Practice Fall Final Exam Questions
... Multiple Choice Questions 1) b 2) b 3) a 4) a 5) a 6) d 7) c 8) b 9) b 10) b 11) b 12) a 13) d 14) c 15) d 16) b 17) d 18) d 19) c 20) b 21) a 22) a 23) b 24) a 25) c 26) a 27) a 28) c 29) a 30) b 31) b 32) b 33) a 34) b 35) c 36) c 37) d 38) b 39) a 40) c 41) a 42) b 43) c 44) a 45) c 46) d 47) b 4 ...
... Multiple Choice Questions 1) b 2) b 3) a 4) a 5) a 6) d 7) c 8) b 9) b 10) b 11) b 12) a 13) d 14) c 15) d 16) b 17) d 18) d 19) c 20) b 21) a 22) a 23) b 24) a 25) c 26) a 27) a 28) c 29) a 30) b 31) b 32) b 33) a 34) b 35) c 36) c 37) d 38) b 39) a 40) c 41) a 42) b 43) c 44) a 45) c 46) d 47) b 4 ...
Inertial electrostatic confinement
Inertial electrostatic confinement is a branch of fusion research which uses an electric field to heat a plasma to fusion conditions. Electric fields can do work on charged particles (either ions or electrons), heating them to fusion conditions. This is typically done in a sphere, with material moving radially inward, but can also be done in a cylindrical or beam geometry. The electric field can be generated using a wire grid or a non-neutral plasma cloud.