* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter Terms - Jensen English Academy! (JEA)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
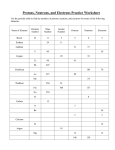
Science 10 - Chapter 4.1 Important Terms Compound (pg. 168) Pure substance made of two or more atoms joined in a specific way BUT it must have at least TWO DIFFERENT ELEMENTS. All compounds are molecules (NaCL) but not all molecules are Compounds (H2O or O2) Atom (pg. 168) Smallest particle of an element that keeps the properties of that element. Made up of protons & neutrons (nucleus) and electrons (surrounding the nucleus). (See Figure 4.2 on pg. 170) Chemical Changes (pg. 168) Changes in the ways atoms and molecules in a pure substance are arranged and interconnected Subatomic Particles (pg. 170) Particles that make up an atom (protons, neutrons and electrons). See discussion of Atomic Theory on page 170 Protons (pg. 170) Subatomic particle with a +1 electric charge Electrons (pg. 170) Subatomic particle with no electric charge Neutrons (pg. 170) Subatomic particle with a -1 electric charge Nuclear Charge (pg. 171) Term given to electric charge on the nucleus. Simply count protons. The nuclear charge is the same as the ATOMIC NUMBER Atomic Number (pg. 171) Same as NUCLEAR CHARGE in a NEUTRAL ATOM Period (pg. 171) Used at the end of this sentence. Also, a left to right row on the periodic table Group or Family (pg. ) A top to bottom column on a periodic table Ions (pg. 173) Charged particles made when atoms gain or lose electrons or protons. METALS lose electrons and form CATIONS. When NON-METALS gain an electron they become ANIONS Multivalent (pg. 173) Metals that can form ions in more than one way (ex. Iron (Fe) can be +2 or +3) Bohr Diagram (pg. 174) A diagram that shows how many electrons are in shells surrounding the nucleus Stable Octet (pg. 175) 8 electrons in the outer shell (Stable = calm, Octet = 8) Valence Shell (pg. 175) Outermost shell that contains electrons Valence Electrons (pg. 175) Electrons in the valence shell and are what is used in chemical bonding Ionic Bonding (pg. 176) One or more electrons TRANSFERS from each atom of the metal to each atom of the non-metal Covalent Bonding (pg. 177) Atoms overlap slightly and unpaired electrons will pair together Covalent Compound (pg. 177) Compound of 2 NON-METALLIC atoms join and share electrons Bonding Pair (pg. 177) The pair of electrons involved in a covalent bond Lone Pair (pg. 177) A pair of electrons NOT used in bonding Lewis Diagram (pg. 178) Illustrates CHEMICAL BONDING by showing only an atom`s valence electrons and the chemical symbol Diatomic Molecule (pg. 180) A pair of the same atoms are joined by covalent bonds (O2) Also Remember: A) Important when we are done Chapter 4 to be able to: a) distinguish between atoms, ions and molecules b) describe arrangement of electrons in atoms, ions and molecules c) write names of formulas for ionic and covalent compounds d) balance chemical equations e) explain the law of conservation of mass as applied to chemical reactions B) For atoms with less than 30 protons, neutrons are about the same number. However as protons are added beyond 30, there will always be more neutrons than protons, thus these are heavier atoms. Extra neutrons help to make the nucleus more stable by keeping the protons as far apart as possible. Heavier atoms are MORE UNSTABLE because the REPULSION between PROTONS is so high C) Electric charge of a nucleus is always POSITIVE because of presence of protons D) Metals are on left side of periodic table, non-metals are on the right. Metalloids make a staircase E) Elements in the same chemical group have similar chemical properties F) Electrons determine a) What properties elements in the same group/family share and b) Predict the kids of compounds that are likely to form G) Forming Compounds: Metals lose an electron and become cations. Non-Metals gain an electron and become anions. Atoms may share electrons! H) Ionic Bonding: Usually the result of a METAL and a NON-METAL joining. One or more electrons transfer from each atom of the metal to the non-metal I) Covalent Bonding: Result of two NON-METALS joining and sharing electrons J) Lewis Diagram ONLY shows VALENCE ELECTRONS and CHEMICAL SYMBOL. Bohr Diagram shows NUCLEUS and ALL ELECTRONS. K) See explanation of Lewis Diagrams and ionic, covalent and diatomic