B. - Physicsland
... A certain isotope has a half-life of 10 years. This means the amount of that isotope remaining at the end of 10 years will ...
... A certain isotope has a half-life of 10 years. This means the amount of that isotope remaining at the end of 10 years will ...
Current Status of Nuclear Physics Research
... The tunnel effect is responsible for the long time scale of stellar burning. Without tunneling there would be no stars as we know them. It is not a coincidence that all main physics related to the understanding of how stars shine occurred in parallel with advances in Nuclear Physics. The more we lea ...
... The tunnel effect is responsible for the long time scale of stellar burning. Without tunneling there would be no stars as we know them. It is not a coincidence that all main physics related to the understanding of how stars shine occurred in parallel with advances in Nuclear Physics. The more we lea ...
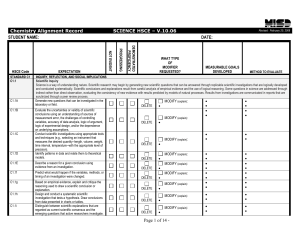
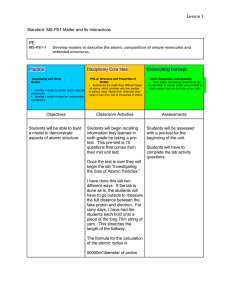
Physical Science Standards
... 2.2 explore matter in terms of specific properties . Performance Indicators State (SPI) and Teacher (TPI): At Level 1, the student is able to SPI distinguish among the phases of matter in terms of volume, shape, and particle arrangement, given illustrations. TPI describe and illustrate the differenc ...
... 2.2 explore matter in terms of specific properties . Performance Indicators State (SPI) and Teacher (TPI): At Level 1, the student is able to SPI distinguish among the phases of matter in terms of volume, shape, and particle arrangement, given illustrations. TPI describe and illustrate the differenc ...
chemistry - My Study materials – Kumar
... Molecule is the smallest particle of a compound. Atoms exist in free states in the form of molecule. A molecule may be formed by the combination of two or more similar atoms of an element, such asoxygen molecule is formed by the combination of two oxygen atoms, molecule of hydrogen which is formed b ...
... Molecule is the smallest particle of a compound. Atoms exist in free states in the form of molecule. A molecule may be formed by the combination of two or more similar atoms of an element, such asoxygen molecule is formed by the combination of two oxygen atoms, molecule of hydrogen which is formed b ...
Chem 11 Review Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 23. Compared to the stability of the original atom, the stability of its ion that resembles a noble gas configuration would be __. a) identical b) sometimes less c) less d) greater 24. Which of the following does NOT affect the ionization energy of an electron? a) the distance of the electron from t ...
... 23. Compared to the stability of the original atom, the stability of its ion that resembles a noble gas configuration would be __. a) identical b) sometimes less c) less d) greater 24. Which of the following does NOT affect the ionization energy of an electron? a) the distance of the electron from t ...
INTRODUCTORY NUCLEAR PHYSICS
... the current era (the recently discovered “heavy” decay modes, such as 14C, double P decay, P-delayed nucleon emission, Mossbauer effect, and so on). The third unit surveys nuclear reactions, including fission and fusion and their applications. The final unit deals with topics that fall only loosely ...
... the current era (the recently discovered “heavy” decay modes, such as 14C, double P decay, P-delayed nucleon emission, Mossbauer effect, and so on). The third unit surveys nuclear reactions, including fission and fusion and their applications. The final unit deals with topics that fall only loosely ...
File
... unstable or radioactive. Radioactive isotopes emit nuclear radiation in the form of rapidly moving particles or high energy electromagnetic waves. The particles are emitted from the nucleus itself and their removal results in changing the atom from one isotope to another. This change may occur once ...
... unstable or radioactive. Radioactive isotopes emit nuclear radiation in the form of rapidly moving particles or high energy electromagnetic waves. The particles are emitted from the nucleus itself and their removal results in changing the atom from one isotope to another. This change may occur once ...
Review Study Guide for the Final
... What is it called when you have more electrons than protons? ...
... What is it called when you have more electrons than protons? ...
2 Atoms and Molecules
... that a minimum of 115 different kinds of atoms exist. Eighty-eight of the elements are naturally occurring and therefore are found in Earth’s crust, oceans, or atmosphere. The others are synthetic elements produced in the laboratory. Each element can be characterized and identified by its unique set ...
... that a minimum of 115 different kinds of atoms exist. Eighty-eight of the elements are naturally occurring and therefore are found in Earth’s crust, oceans, or atmosphere. The others are synthetic elements produced in the laboratory. Each element can be characterized and identified by its unique set ...
Electron - CoolHub
... known universe is made from. It’s kind of like the alphabet in which only 26 letters, in different combinations, make up many thousands of words. The 100 or so atoms of the periodic table, in different combinations, make up millions of different substances. Note: It is often confusing for students t ...
... known universe is made from. It’s kind of like the alphabet in which only 26 letters, in different combinations, make up many thousands of words. The 100 or so atoms of the periodic table, in different combinations, make up millions of different substances. Note: It is often confusing for students t ...