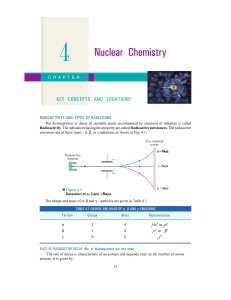
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... TRUE/FALSE. Write ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if the statement is false. 47) Gamma radiation only changes the atomic number but not the mass number of a nucleus. 48) The neutron/proton ratio of stable nuclei increases with increasing atomic number . 49) The energy produced by the sun is the ...
... TRUE/FALSE. Write ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if the statement is false. 47) Gamma radiation only changes the atomic number but not the mass number of a nucleus. 48) The neutron/proton ratio of stable nuclei increases with increasing atomic number . 49) The energy produced by the sun is the ...
Unit 2 Lesson 3
... • Isotopes of the same element have different numbers of neutrons and from that, different mass numbers. • Carbon atoms have 6 protons and 6 neutrons in their nucleus, giving them an atomic mass of 12 • When carbon atoms lose or gain neutrons, they become isotopes. • The mass number is added to the ...
... • Isotopes of the same element have different numbers of neutrons and from that, different mass numbers. • Carbon atoms have 6 protons and 6 neutrons in their nucleus, giving them an atomic mass of 12 • When carbon atoms lose or gain neutrons, they become isotopes. • The mass number is added to the ...
Atomic structure and periodic table
... It can donate the three outer electrons to have stable electronic structure/configuration 2:8. It can gain five extra electrons to have stable electronic structure/configuration 2:8:8. Donating requires less energy, and thus Aluminium reacts by donating its three outer electrons. Elements with less ...
... It can donate the three outer electrons to have stable electronic structure/configuration 2:8. It can gain five extra electrons to have stable electronic structure/configuration 2:8:8. Donating requires less energy, and thus Aluminium reacts by donating its three outer electrons. Elements with less ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. H2O ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. H2O ...
1920
... massive nucleus of small dimensions. It was suggested by Van den Broekf that the scattering of a-particles by the atoms was not inconsistent with the possibility that the charge on the nucleus was equal to the atomic number of to the ...
... massive nucleus of small dimensions. It was suggested by Van den Broekf that the scattering of a-particles by the atoms was not inconsistent with the possibility that the charge on the nucleus was equal to the atomic number of to the ...
Wednesday, Oct. 5, 2016
... • Since neutrons are heavier than protons, they can decay to a proton in a free space – On the other hand, protons are lighter than neutrons therefore they can only undergo a b-decay within a nucleus – Lifetime of a neutron is about 900sec – This lifetime is a lot longer than nuclear reaction time s ...
... • Since neutrons are heavier than protons, they can decay to a proton in a free space – On the other hand, protons are lighter than neutrons therefore they can only undergo a b-decay within a nucleus – Lifetime of a neutron is about 900sec – This lifetime is a lot longer than nuclear reaction time s ...
Chemistry Entrance Material for Grade 11 to 12 Answer Key
... Why CaCl2 solution conducts current but sugar in water does not 98. Why does aqueous CaCl2 solution conduct electricity but sugar in water does not? Which of the following is a part of the explanation? [-A-] Sugar solution in water forms only one type of ion: Sugar (aq). [-B-] Calcium chloride forms ...
... Why CaCl2 solution conducts current but sugar in water does not 98. Why does aqueous CaCl2 solution conduct electricity but sugar in water does not? Which of the following is a part of the explanation? [-A-] Sugar solution in water forms only one type of ion: Sugar (aq). [-B-] Calcium chloride forms ...
High School Knowledge Exam – Study Guide
... -Atomic radii decrease left to right (due to increasing number of protons to attract electrons yet no change in number of energy levels) -Atomic radii increase top to bottom (due to increased number of energy levels, thus increasing distance of outer electrons from nucleus, resulting in less attract ...
... -Atomic radii decrease left to right (due to increasing number of protons to attract electrons yet no change in number of energy levels) -Atomic radii increase top to bottom (due to increased number of energy levels, thus increasing distance of outer electrons from nucleus, resulting in less attract ...
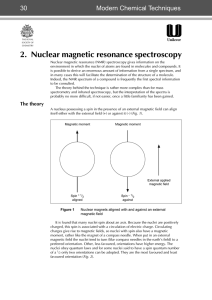
2. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
... In the analysis of an organic sample it is the 1H- or proton-NMR spectrum that is usually most useful because hydrogen atoms are present in such large numbers, bonded in a variety of environments. However, from the theory presented so far one would expect that all hydrogen atoms would resonate at th ...
... In the analysis of an organic sample it is the 1H- or proton-NMR spectrum that is usually most useful because hydrogen atoms are present in such large numbers, bonded in a variety of environments. However, from the theory presented so far one would expect that all hydrogen atoms would resonate at th ...
2 - TEST BANK 360
... nitrogen oxides associated with smog are prime examples. Statement (c) is false; ionic compounds consist of anions and cations. Statement (d) is very close to the right selection but it is too restrictive. Some molecular compounds containing both metal and nonmetal atoms are known to exist, e.g., ci ...
... nitrogen oxides associated with smog are prime examples. Statement (c) is false; ionic compounds consist of anions and cations. Statement (d) is very close to the right selection but it is too restrictive. Some molecular compounds containing both metal and nonmetal atoms are known to exist, e.g., ci ...
FE Exam review for Chemistry
... physical & chemical properties of that matter. An element is a type of atom with a defined number of p, n & e-. What are the three subatomic particles? What do you know about each? Protons = + charge, mass of 1 amu, in the nucleus Neutron = no charge, mass of 1 amu, in the nucleus Electrons = - char ...
... physical & chemical properties of that matter. An element is a type of atom with a defined number of p, n & e-. What are the three subatomic particles? What do you know about each? Protons = + charge, mass of 1 amu, in the nucleus Neutron = no charge, mass of 1 amu, in the nucleus Electrons = - char ...
transmutation of nuclides
... science and technology in many applications. In radioactive decay processes, some of the things are conserved, meaning they do not change. The number of nucleons before and after the decay is the same (conserved). So are electric charges and energy (including mass). The relationship between nuclides ...
... science and technology in many applications. In radioactive decay processes, some of the things are conserved, meaning they do not change. The number of nucleons before and after the decay is the same (conserved). So are electric charges and energy (including mass). The relationship between nuclides ...
Radioactive Decays – transmutations of nuclides
... In radioactive decay processes, some of the things are conserved, meaning they do not change. The number of nucleons before and after the decay is the same (conserved). So are electric charges and energy (including mass). The relationship between nuclides is best seen in a chart based on the number ...
... In radioactive decay processes, some of the things are conserved, meaning they do not change. The number of nucleons before and after the decay is the same (conserved). So are electric charges and energy (including mass). The relationship between nuclides is best seen in a chart based on the number ...
Subatomic Physics: the Notes - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... By this time the electric charge of the electron had been measured (through the Millikan oil-drop experiment of 1909) and so it was known that the electron had a charge equal in size to (but opposite in sign from) the charge, q = e, of the Hydrogen ion (what we now call the Hydrogen nucleus, or pro ...
... By this time the electric charge of the electron had been measured (through the Millikan oil-drop experiment of 1909) and so it was known that the electron had a charge equal in size to (but opposite in sign from) the charge, q = e, of the Hydrogen ion (what we now call the Hydrogen nucleus, or pro ...
lectures on subjects in physics, chemistry and biology
... pressure it is found that the current is carried by electrons moving in one direction and positively charged atoms moving in the opposite direction. T h e stream of positively charged atoms can be allowed to pass through a hole in the negative electrode and so may be separated from the stream of ele ...
... pressure it is found that the current is carried by electrons moving in one direction and positively charged atoms moving in the opposite direction. T h e stream of positively charged atoms can be allowed to pass through a hole in the negative electrode and so may be separated from the stream of ele ...