39 The Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... • When two nucleons are just a few nucleon diameters apart, the nuclear force they exert on each other is nearly zero (small force vectors). • This means that if nucleons are to be held together by the strong force, they must be held in a very small volume. • Nuclei are tiny because the nuclear forc ...
... • When two nucleons are just a few nucleon diameters apart, the nuclear force they exert on each other is nearly zero (small force vectors). • This means that if nucleons are to be held together by the strong force, they must be held in a very small volume. • Nuclei are tiny because the nuclear forc ...
File
... generated during processing. Any nuclear process involves the manufacture of nuclear waste whether they are low level (gloves, cotton balls, hospital gowns) or high level (spent nuclear fuel rods) waste products. Concern about the management of nuclear waste materials has caused much controversy and ...
... generated during processing. Any nuclear process involves the manufacture of nuclear waste whether they are low level (gloves, cotton balls, hospital gowns) or high level (spent nuclear fuel rods) waste products. Concern about the management of nuclear waste materials has caused much controversy and ...
31.1 Nuclear Structure
... •In 1949, Willard Libby developed a method of using the radioactive isotope 14 C to determine the age of organic materials up to about 50,000 years old. Libby won a Nobel Prize for his work. •The concentration of 14 C in the is about 1 part per trillion (1 atom of 14 C for 8.3 x 1011 atoms of 12 C. ...
... •In 1949, Willard Libby developed a method of using the radioactive isotope 14 C to determine the age of organic materials up to about 50,000 years old. Libby won a Nobel Prize for his work. •The concentration of 14 C in the is about 1 part per trillion (1 atom of 14 C for 8.3 x 1011 atoms of 12 C. ...
Chapter 37
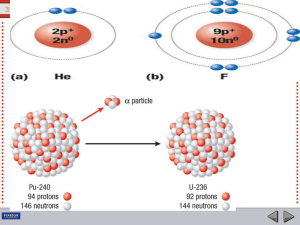
... electromagnetic radiation (pure energy) similar to x rays, but higher in energy and shorter in wavelength. – Alpha and beta radiation are matter; contains p, n, or e while gamma is pure energy (no p, n, e). – Highly energetic, the most penetrating form of radiation (barriers of lead, concrete, or mo ...
... electromagnetic radiation (pure energy) similar to x rays, but higher in energy and shorter in wavelength. – Alpha and beta radiation are matter; contains p, n, or e while gamma is pure energy (no p, n, e). – Highly energetic, the most penetrating form of radiation (barriers of lead, concrete, or mo ...