Chapter 4 and 5
... - truncate if preceding digit is even Why? Long strings of numbers would become very wrong. Go through handout together. HW finish handout ...
... - truncate if preceding digit is even Why? Long strings of numbers would become very wrong. Go through handout together. HW finish handout ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... Beta particles are identical to electrons and thus have a charge of (1). This type of decay process leaves the mass number of the nuclei unchanged. A beta particle is minute in comparison to that of an alpha particle and has about one hundred times the penetrating ability. Where an alpha particle ca ...
... Beta particles are identical to electrons and thus have a charge of (1). This type of decay process leaves the mass number of the nuclei unchanged. A beta particle is minute in comparison to that of an alpha particle and has about one hundred times the penetrating ability. Where an alpha particle ca ...
An Unifying Basis for all the Nuclear Reactions
... already in an expanded form as a gas at the room temperature. They can't release any more energy when they are subjected to any kind of nuclear reactions. To make the hydrogen atoms to release energy, first we need to compress the atoms to the state of plasma and then that plasma should be subjected ...
... already in an expanded form as a gas at the room temperature. They can't release any more energy when they are subjected to any kind of nuclear reactions. To make the hydrogen atoms to release energy, first we need to compress the atoms to the state of plasma and then that plasma should be subjected ...
Chapter 16 Atomic Energy
... nucleus of an atom. It differs from a chemical reaction in several ways. • One difference is that chemical reactions do not change the mass of atoms, but nuclear reactions do so by a very small amount. • A small amount of mass can change into a large amount of energy, because energy is equal to mass ...
... nucleus of an atom. It differs from a chemical reaction in several ways. • One difference is that chemical reactions do not change the mass of atoms, but nuclear reactions do so by a very small amount. • A small amount of mass can change into a large amount of energy, because energy is equal to mass ...
Chapter 32 Applied Nucleonics
... the heavy nuclei like uranium. This corresponds to the mass difference that accounts for an energy release of about 1 MeV for each nucleon involved in the process. The fission reactions that were studied first involved the use of the neutron bombardment of the fissionable material. The theoretical e ...
... the heavy nuclei like uranium. This corresponds to the mass difference that accounts for an energy release of about 1 MeV for each nucleon involved in the process. The fission reactions that were studied first involved the use of the neutron bombardment of the fissionable material. The theoretical e ...
The Strong Nuclear Force and the Stability of the Nucleus
... ● The JET (Joint European Torus) project was set up to carry out research into fusion power. ● It has yet to generate a self-sustaining fusion reaction. ● The main problem is getting two nuclei close enough for long enough for them to fuse. ...
... ● The JET (Joint European Torus) project was set up to carry out research into fusion power. ● It has yet to generate a self-sustaining fusion reaction. ● The main problem is getting two nuclei close enough for long enough for them to fuse. ...
nuclear physics - review
... ● The JET (Joint European Torus) project was set up to carry out research into fusion power. ● It has yet to generate a self-sustaining fusion reaction. ● The main problem is getting two nuclei close enough for long enough for them to fuse. ...
... ● The JET (Joint European Torus) project was set up to carry out research into fusion power. ● It has yet to generate a self-sustaining fusion reaction. ● The main problem is getting two nuclei close enough for long enough for them to fuse. ...
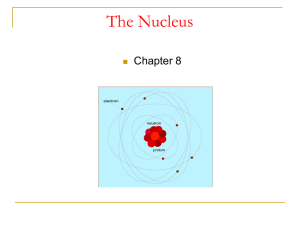
CH_8_nucleus_new
... be exerted upon them to cause such large deflections. Rutherford found that the only way to explain the deflections was to picture an atom with a tiny nucleus in which positive charge existed and nearly all the mass existed; And the electrons were some distance away from the nucleus. In other words, ...
... be exerted upon them to cause such large deflections. Rutherford found that the only way to explain the deflections was to picture an atom with a tiny nucleus in which positive charge existed and nearly all the mass existed; And the electrons were some distance away from the nucleus. In other words, ...
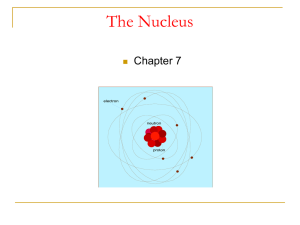
7.2- Nuclear reactions (PPT)
... Returning to the BE / A graph we see that iron (Fe) is the most stable of the nuclei. Nuclear fusion will occur with the elements below Fe because joining smaller nuclei forms bigger ones, which are higher on the graph (and thus more stable). Nuclear fission will occur with the elements above Fe ...
... Returning to the BE / A graph we see that iron (Fe) is the most stable of the nuclei. Nuclear fusion will occur with the elements below Fe because joining smaller nuclei forms bigger ones, which are higher on the graph (and thus more stable). Nuclear fission will occur with the elements above Fe ...