* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 Nature
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Irving Gottesman wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
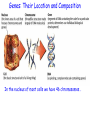
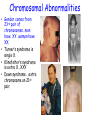
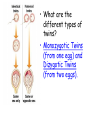
Nature vs. Nurture The Nature Argument (is sometimes compelling) This guy will never be…. This guy!!! Why does Brad Pitt look the way he does? Behavior Genetics: The study of the power and limitations of genes AND environment on who we are. Genes: Our Biological Blueprint Genes: Their Location and Composition In the nucleus of most cells we have 46 chromosomes… Except… Sperm and Eggs Chromosome Breakdown Chromosomes (books) DNA (pages) Genes (words) Nucleotides (letters) What do we get from our parents? • We inherit one set of 23 chromosomes from each parent. • The two sets form pairs that contain alternate genes for the same traits. • Sometimes, one gene is dominant and “overrides” the recessive gene. What do we get from our parents? • Let’s take eye color. • In humans, brown eyes are dominant over blue eyes. If a couple who are both heterozygous for brown eyes reproduce with one another, what are the chances of the child having blue eyes? • What if one parent is heterozygous and one is homozygous? Other Dominant Traits • Curly hair. • Unattached earlobes. • Farsightedness. Chromosomal Abnormalities • Gender comes from 23rd pair of chromosomes…men have XY…woman have XX. • Turner’s syndrome is single X. • Klinefelter’s syndrome is extra X…XXY • Down syndrome….extra chromosome on 21st pair. Genetic Similarities 99.9% Mrs. Stout is 96% 99.9% Identical Twins • Best way to really study genetics because they come from the same zygote. • Bouchard Study • .69 Correlational coefficient for IQ tests of identical twins raised apart. • .88 raised together. • What are the different types of twins? • Monozygotic Twins (from one egg) and Dizygotic Twins (from two eggs). Twin Studies: The results • To summarize the countless amount of studies: Twins (especially identical), whether or not they are raised in the same environment are very much alike in many ways. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qw3S35wGgT8 Temperament • A person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity. • It remains relatively stable over time. Heritability • The proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes. • It is a mathematical formula. • Ranges from 1 (all variance due to heredity - like tongue curling) to 0 (none due to heredity – like speaking English). • As environments become more similar, heredity as a source of differences becomes more important. • Mark Twain explains it best using the barrel example. Heritability and Disease Evolutionary Psychology • The goal of human behavior is to perpetuate the gene pool. Evolutionary Psychology & Natural Selection • 1959 Russian Fox story. • 40 Males, 100 Femalesmated - then kept only tamest of bunch. • Mated the tames. • 40 years later… • New Breed of Fox! Evolutionary Psychology at Work If we wanted to create a whole population of brainy people, we could take some people like… Have them mate. Then have the brainiest offspring mate amongst each other, and for countless generations keep doing the same thing. After 200 years, what would the population be like or what are the chances that the 40th generation of offspring be brainy? Genetic Diversity • The best source of genetic diversity comes from genetic mutations and new gene combinations produced at each human conception. • A mutation is a random error in gene replication that leads to a change. Look at our Behaviors… Evolutionary psychologists would ask these questions? • Why do infants fear strangers when they become mobile? • Why are most parents devoted to their children? • Why do we have more phobias about spiders and snakes than electricity and nuclear weapons? Now, the big one? How and why do men and women differ sexually? Of course, there are other differences… Sexuality and the Evolutionary Psychologist • Casual sex is more accepted by men. • When average men and women randomly ask strangers for sex tonight, 75% of men agreed, almost no women agreed. WHY? Sperm is Cheap Eggs are Not What do men and women want? (According to Evolutionary Psychology) Men want: • Healthy • Young • Waist 1/3 narrower than hips (a sign of future fertility) Women want: • Wealth • Power • Security Can this change? Nature vs. Nurture What do you think so far? Does Nature and Nurture interact and grow off of each other? Next time, we will look at Nurture in detail…